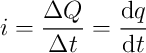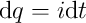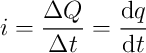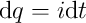Module 05
Current and Resistance
Last Updated: Fri Sep 27 10:15:33 AM CDT 2024
Current
- Current is just charge that moves.
- Current has units of coulombs per second, so we could write it as
the derivative of charge.
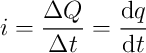
OR
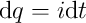
If charge is water, then current is current…
Resistors
plinko
boards do a similar thing for balls.
Demo: Current through a resistor
Let’s run some current through some resistors…
- how much current should we get?
- Ohm’s law says : \(V = iR\)
Resistors
- Resistors resist current
- They also dissipate power
plinko
boards do a similar thing for balls.
Electric potential in a circuit
At every point in a circuit, we can measure the electric poetential
with respect to ground.
Very similar to water flowing through a system of pipes.
Dissipated Power
Resistors dissipate electrical power.
The power is either converted to heat, or work, or both.
The power comes from the potential energy of the charge.
Phone Batteries
- Phones have batteries.
- Battery capacities are typically reported in units of mAh
(milliAmpere-hour)
- This is the amount of charge in a milliAmpere current that runs for
1 hour.
Example:
- How much charge does a phone battery move through the phone?
- How much current does a cell phone draw (on average)?
- What is the resistance of a cell phone (most phones use a lithium-ion
battery)?
- How much power does a cell phone use (on average)?
- How much energy is used the phone during a single charge?
- How long does it take to recharge the battery?
Phone Batteries
What is the effective resistance of your phone?
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
Light bulbs are resistors that convert electrical energy into
heat/light.
Incandescent bulbs have a thin wire made of tungsten called a
filament.
The filament gets hot and gives off blackbody
radiation
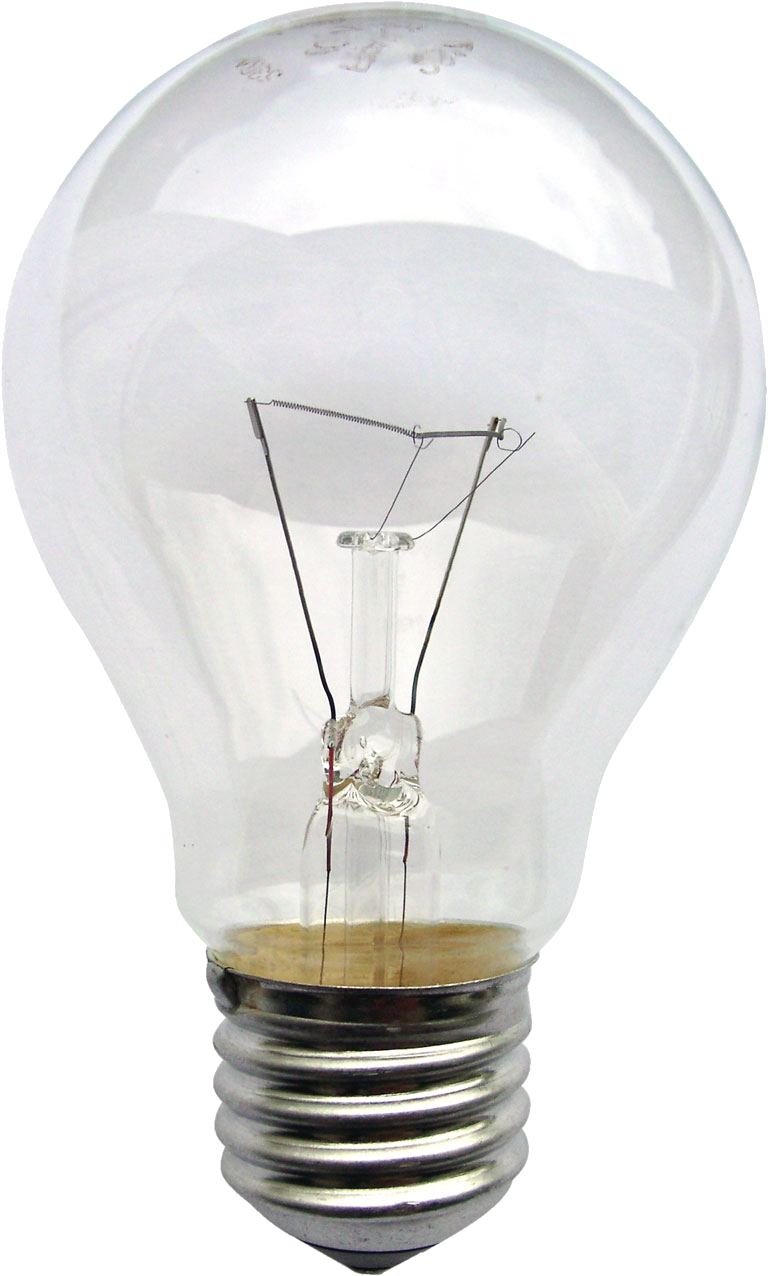

(Old) Light Bulb Examples
What is the
resistance of a 60 W light bulb
- According to Wikipedia:
- A typical 60 W light bulb has a tungsten filament that:
- will uncoil to about 580 mm.
- The filament diameter is about 0.05 mm.
- According to the text
book:
- Tungsten has a resistivity of \(5.6 \times
10^{-8} \;\Omega \text{m}\)
Resistivity
The resistance of a cylinder is
\(R = \frac{\rho L}{A}\)
\(\rho\) is called the resistivity.
It is a property
of the material.
The resistivity for most materials depends on its temperature. For
metals, resistivity goes up with temperature.
\(\rho = \rho_0 ( 1 + \alpha \Delta T
)\)
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
What is the
resistance of a 60 W light bulb
- According to Wikipedia:
- A typical 60 W light bulb has a tungsten filament that:
- will uncoil to about 580 mm.
- The filament diameter is about 0.05 mm.
- According to the text
book:
- Tungsten has a resistivity of \(5.6 \times
10^{-8} \;\Omega \text{m}\)
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
What
is the temperature of the filament in a 60 W light bulb?
A 60 W light bulb dissipates 60 W of power.
- The light bulb produces light by heating up the filament.
- The resistance of the light bulb increases with temperature.
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
How much
current runs through a 60 W light bulb?
A 60 W light bulb dissipates 60 W of power.
The voltage applied to the light bulb is 120 V (in the US)
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
How much
current runs through a 60 W light bulb?
A 60 W light bulb dissipates 60 W of power.
The voltage applied to the light bulb is 120 V (in the US)
0.50 A
Note: most breakers in a home are set to trip at 15 A. So, one
circuit in a breaker box can power 30 60 W light bulbs, or 1800 W.
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
Which
has a larger resistance, a 100 W light bulb, or a 60 W light bulb?
(Old) Light Bulb Examples
Which
has a longer filament, a 100 W light bulb, or a 60 W light bulb
(assuming the diameters are the same)?
Extension Cord Example
“Perfect” Wires
- If we connect resistors in series, their resistances add
together
- Real wires have resistance, which means that the resistance
connected to an emf will be increased by using wires.
- If this resistance is significant, then we explicitly draw them
in our circuit diagram.
Extension Cord Example
- If you use an extension cord with non-zero resistance to plug in
some appliance, the power available to the appliance will be less than
if you just plug it into the wall.
If an appliance uses 1000 W of power when connected to a wall outlet,
how much power will it consume if it is connected to the wall using an
extension cord with a 3 \(\Omega\)
resistance in each wire?
Internal Resistance
What is the internal resistance of our battery?
Last Slide
Last Slide
No really, that was the last one.
Last Slide
There is nothing to see here!
Last Slide
Look, I know that the slide count says there are more slides, but
there aren’t any more.
Last Slide
Seriously, it’s just a bunch of Last Slide slides.
Last Slide
This is the last one that says anything funny. You can stop clicking
now.
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
The hydraulic (water) analogy
An analogy between the flow of water and electrical current can be
made.
Dissipated Power
- Consider the energy that a charge \(dq\) loses as it passes through a
resistor.
- This power is either turned into heat, work, or both.
- Charge is conserved.
Only energy is transferred.
- Does the charge lose kinetic energy or potential energy?