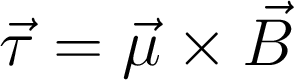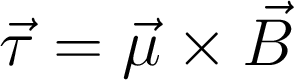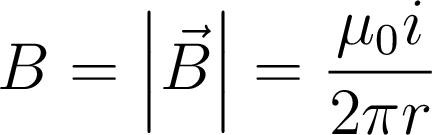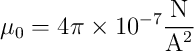Module 08
Last Updated: Thu Apr 4 08:22:11 AM CDT 2024
Magnetic Force on Magnet
A bar magnet will align itself with an external magnetic field.
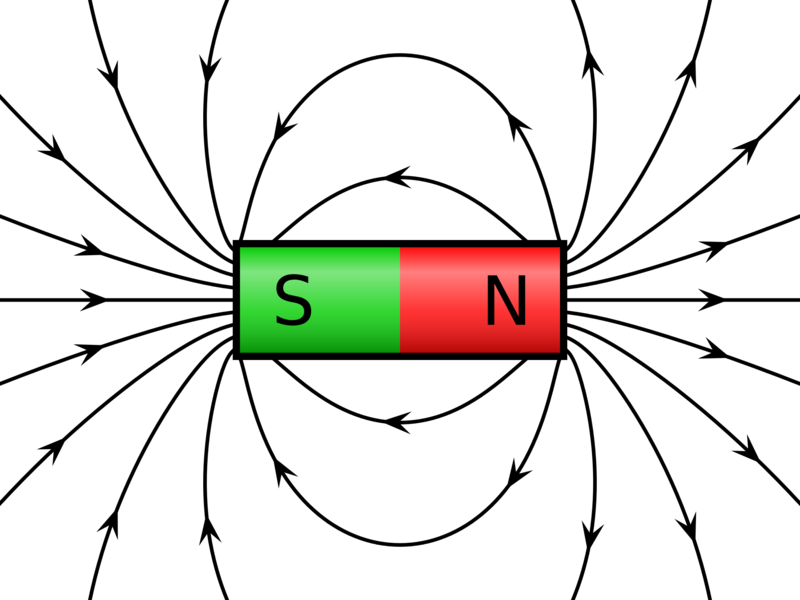
The north pole “wants” to point in the direction of the field.
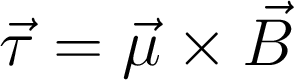
Demo
- A compass needle is just a small magnet.
- It has a north pole (the one that points north), and a south pole (the one that points south).
- Magnets tend to align themselves with external magnetic fields.
Demo: Magnetic Field from Current in a Wire
Demo: Magnetic Field from Current in a Wire
The Source of Magnetic Fields
- Charge produces an electric field.
- Current produces a magnetic field.
- A long straight wire will produce circular magnetic field lines.
- The direction of the field lines is given by a right-hand rule…
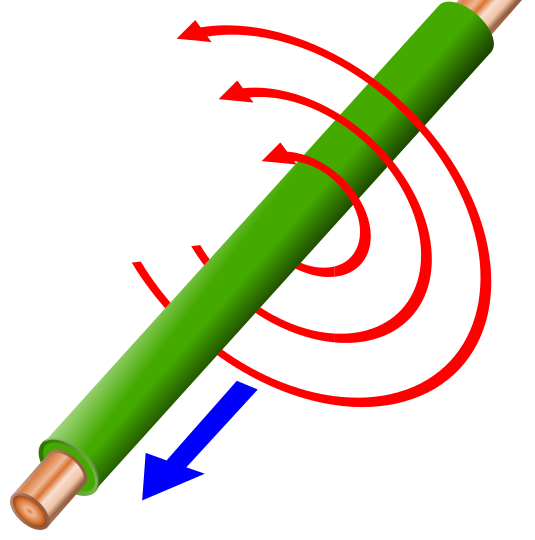
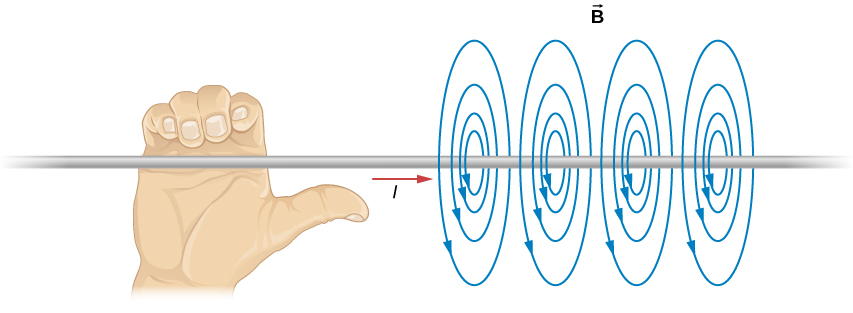
Demo: Right Hand Rule
We can apply the right hand rule to determine the direction that the compass will point.
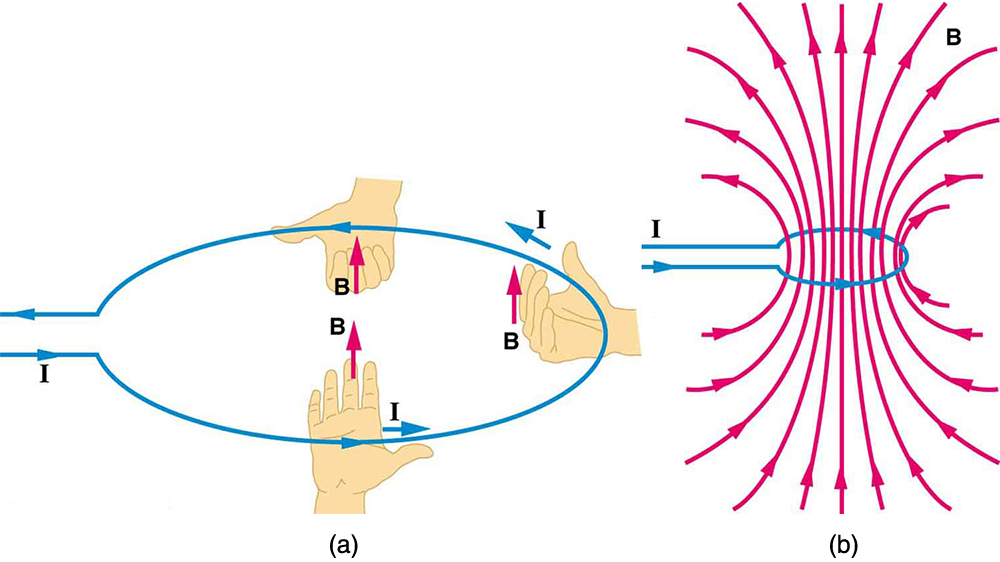
Right-hand Rule for Loop
- We have a new right-hand rule for the direction of a magnetic field produced by current.
- This RHR can be used for current loops as well.
_
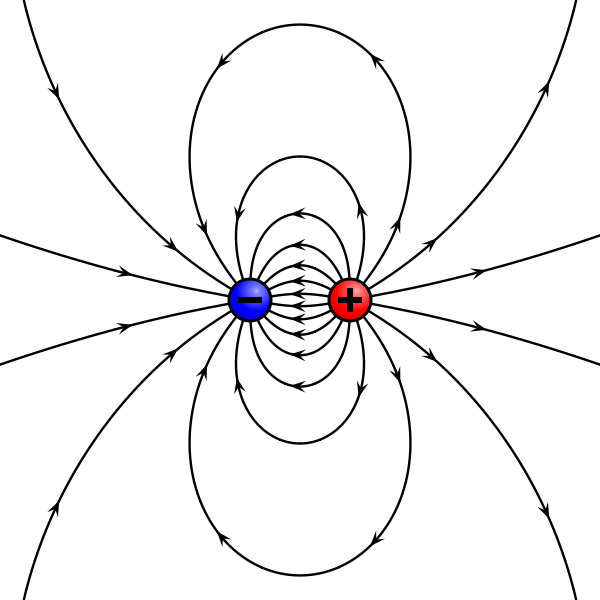
Magnetic “Dipole”
- A loop of current produces magnetic field lines that look like an electric dipole (from the outside)
- Magnetic field lines always form closed loops.
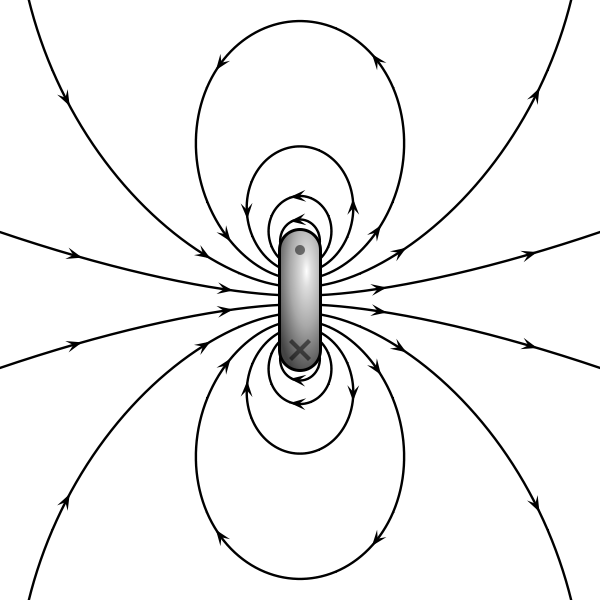
Magnetic “Dipole”
- A bar magnet produces magnetic field lines that look like a current loop.
- The magnetic field lines come out of the north pole and into the south pole.
- Magnetic field lines come out of the north pole and into the south pole.


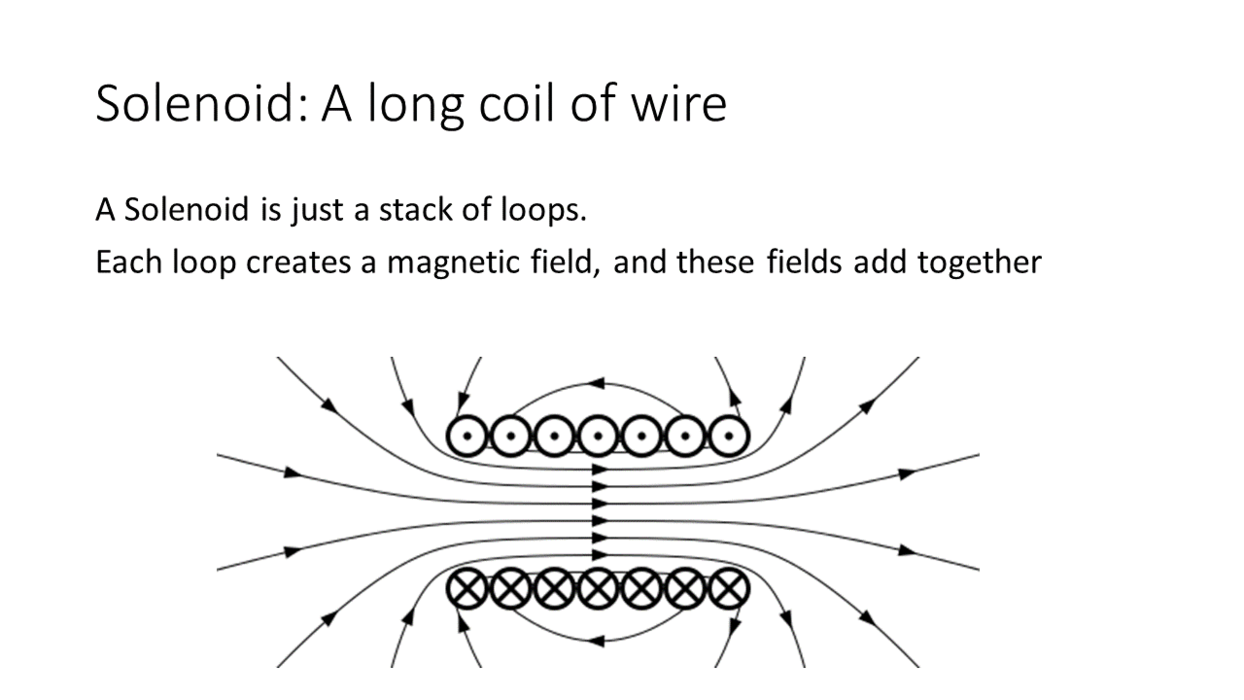
Demo: Magnetic Field from Solenoid
Source of a magnet’s magnetic field
- Matter is made up of many tiny magnetic dipoles.
- If the dipoles are randomly oriented, their magnetic fields will cancel out on average.
- If some dipoles begin to align with each other, they can produce a measurable net magnetic field.
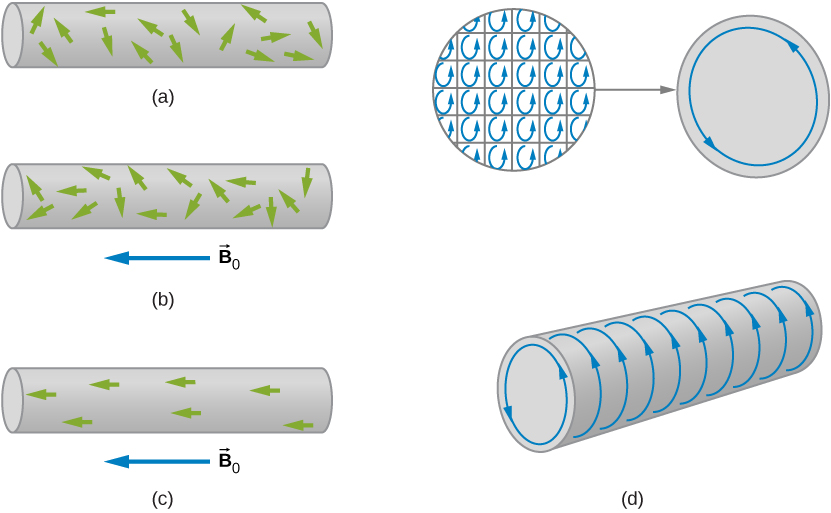
Source of a magnet’s magnetic field
- This is pretty much all we will have to say about this…

Earth’s Magnetic Field
- The earth’s magnetic field looks like a bar magnet.
- The north pole of a magnet is called the north pole because it is attracted to the north pole… so Earth’s north pole is a south pole.
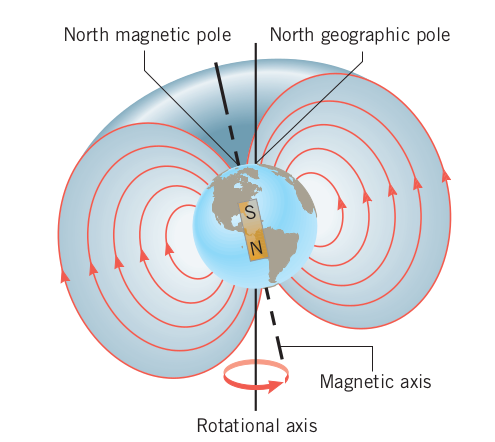
Earth’s Magnetic Field
- The earth’s magnetic field looks like a bar magnet.
- The north pole of a magnet is called the north pole because it is attracted to the north pole… so Earth’s north pole is a south pole.


Earth’s Magnetic Field
- The earth’s magnetic field looks like a bar magnet (actually, it looks like a magnetic dipole).
- The north pole of a magnet is called the north pole because it is attracted to the north pole… so Earth’s north pole is a south pole.


Faraday’s Law
Recall: Maxwell’s Equations
| \[ \nabla \cdot \vec{E} = \frac{\rho}{\epsilon_0} \] |
\[ \oint_S \vec{E} \cdot d\vec{A} = \frac{q_\text{enc}}{\epsilon_0}\] |
| \[ \nabla \cdot \vec{B} = 0 \] |
\[ \oint \vec{B} \cdot d\vec{A} = 0\] |
| \[ \nabla \times \vec{E} = -\frac{\partial\vec{B}}{\partial t} \] |
\[ \oint \vec{E} \cdot d \vec{l} = - \frac{d}{dt} \int_S \vec{B}\cdot d\vec{A}\] |
| \[ \nabla \times \vec{B} = \mu_0 \vec{J} -\mu_0 \epsilon_0 \frac{\partial\vec{E}}{\partial t} \] |
\[ \oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l} = \mu_0 \int_S \vec{J}\cdot d \vec{l} - \mu_0\epsilon_0\frac{d}{dt} \int_S \vec{E}\cdot d\vec{A}\] |
Faraday’s Law
\[ \oint \vec{B} \cdot d \vec{l} = \mu_0 \int_S \vec{J}\cdot d \vec{l} = \mu_0 i_\text{enc}\]
Examples
Example
What magnetic field is produced 1 m away from by a long, straight wire carrying 1 A of current?
Example
Consider the two very long, parallel currents shown below. Determine the magnetic field at any point along the vertical line that passes through the point halfway between the two currents.
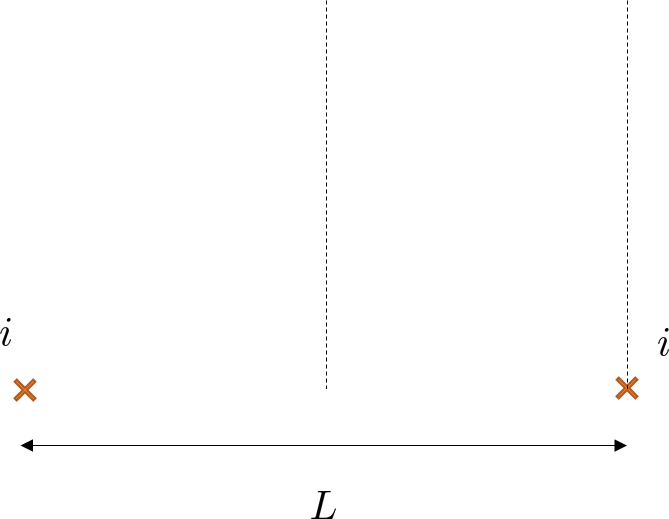
Determine the magnetic field at any point along the vertical line that passes through the right-side current.
- We know that the field strength for each wire will be \(B = \frac{\mu_0 i}{2\pi r}\), but they will add together as vectors…
Example
Consider the two very long, parallel currents shown below. What force will they exert on each other?

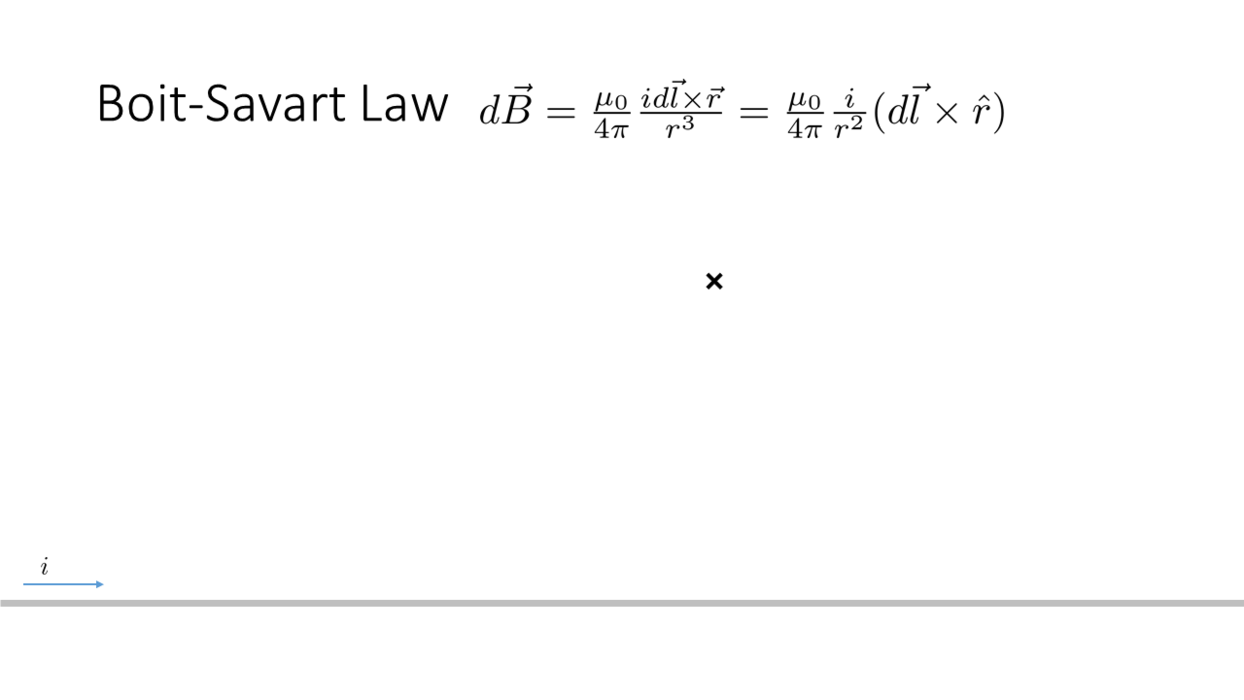
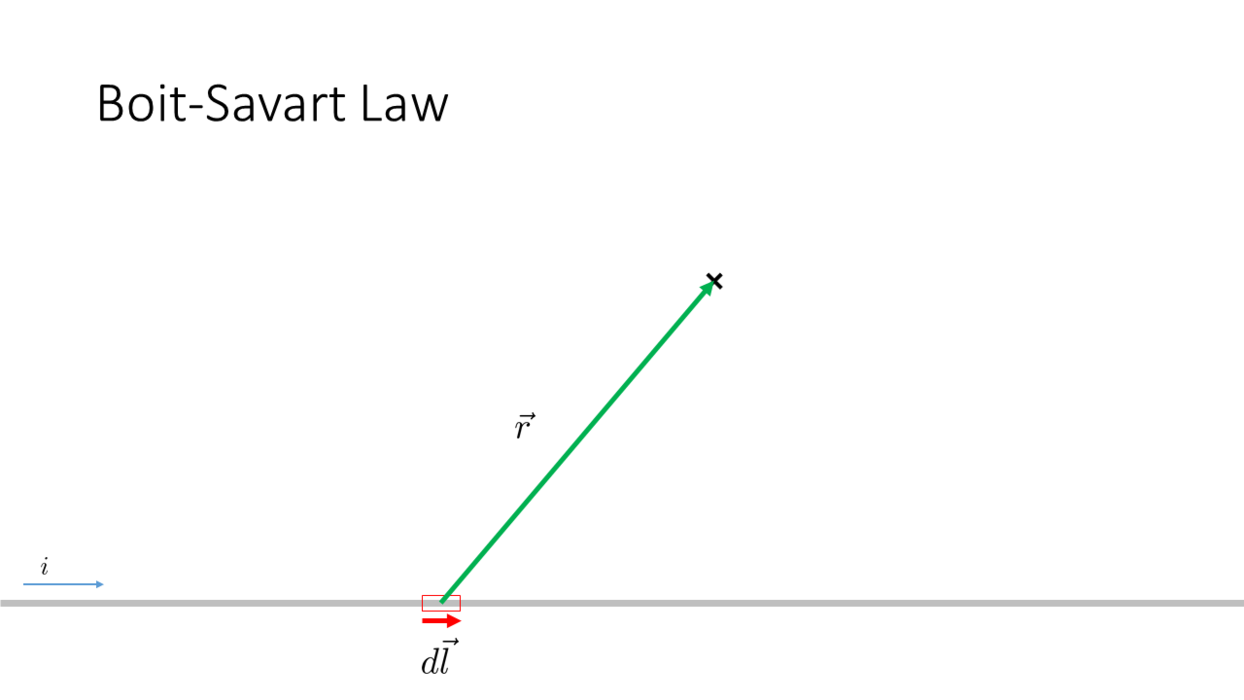
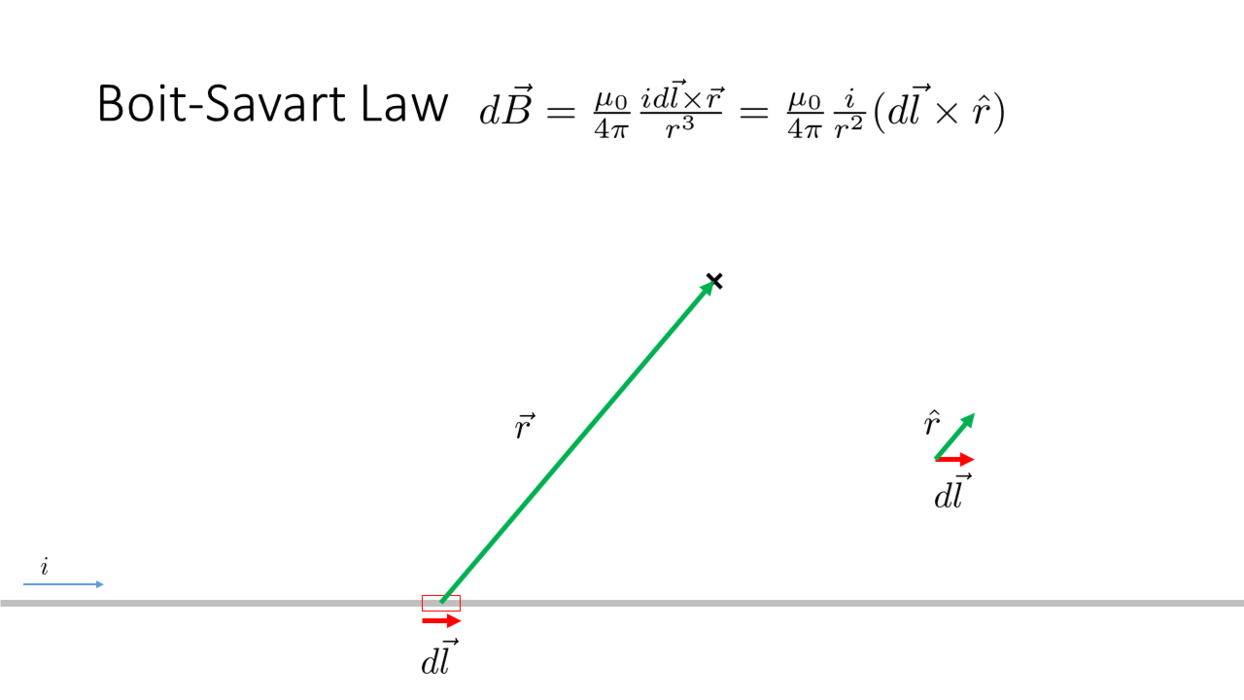
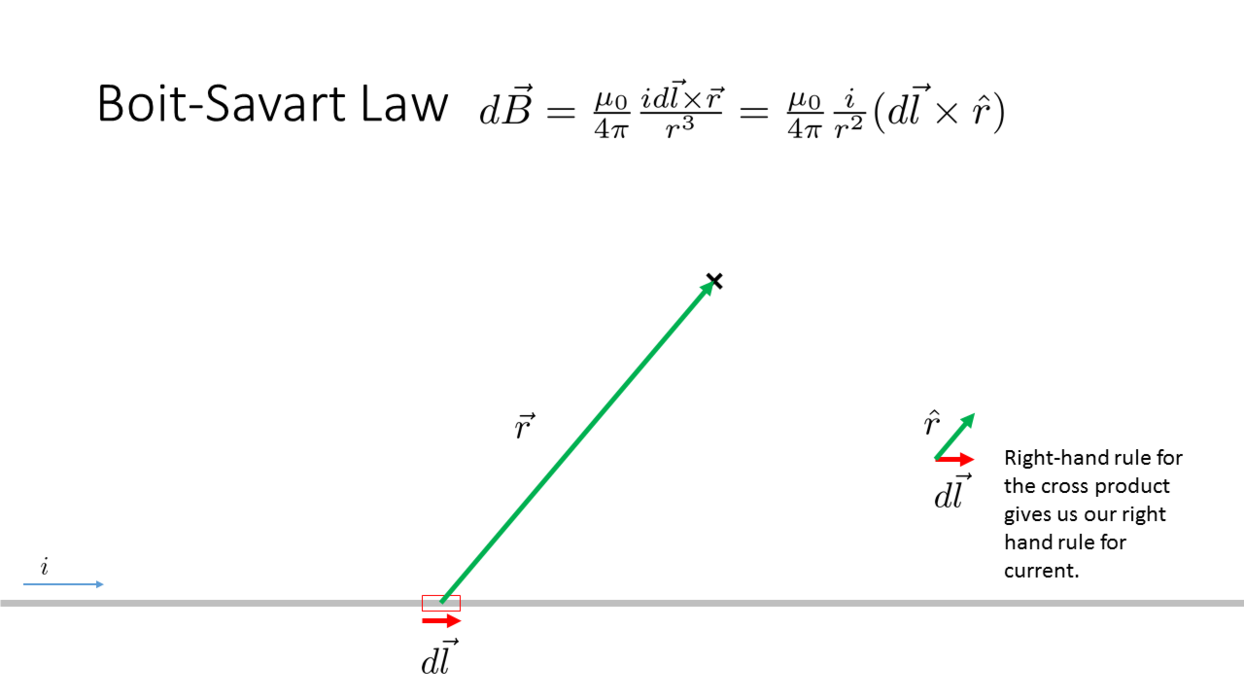
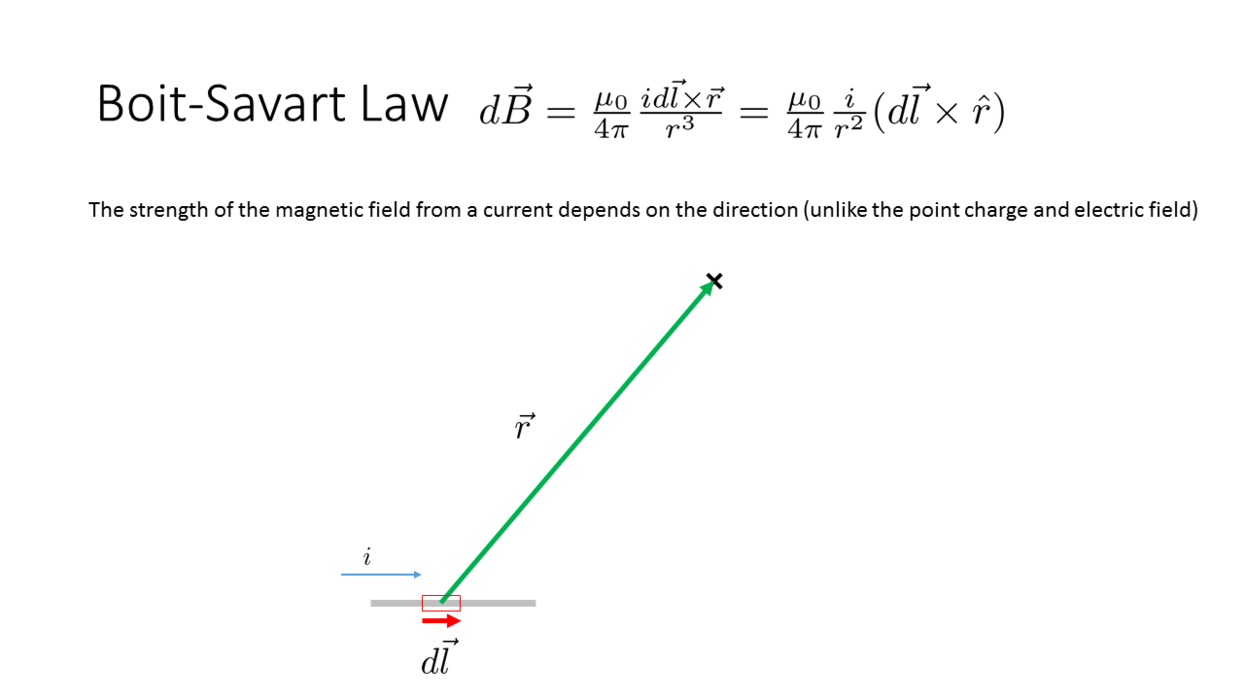
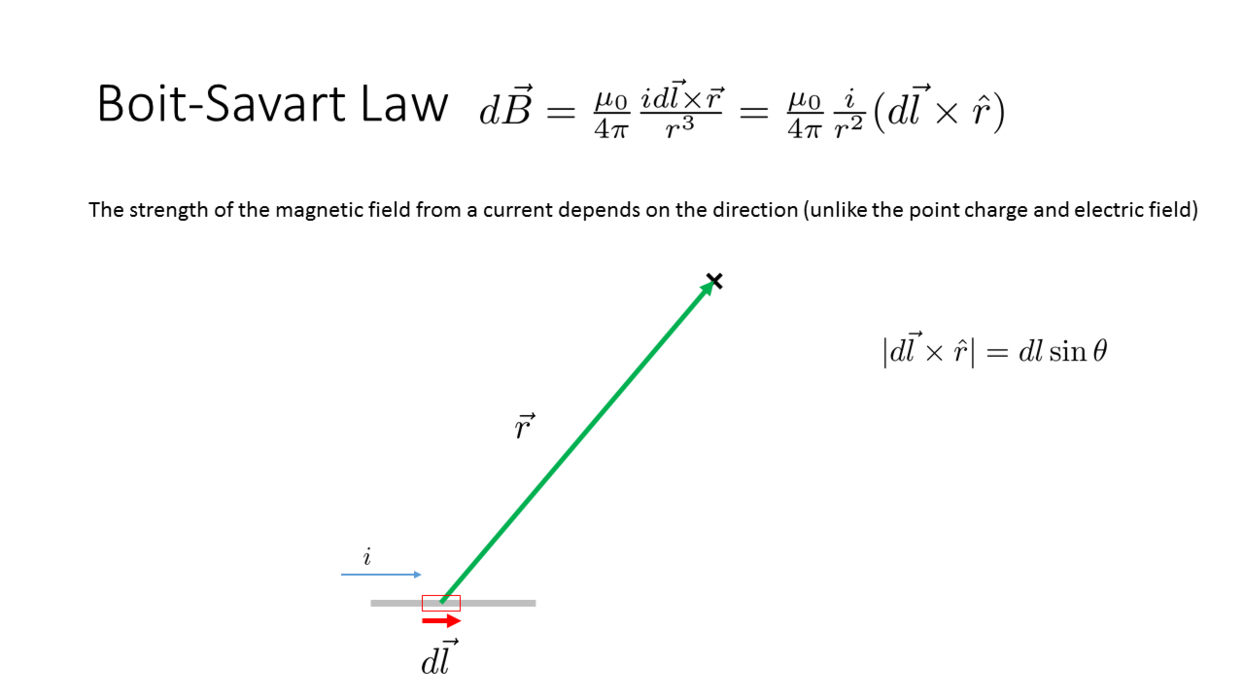
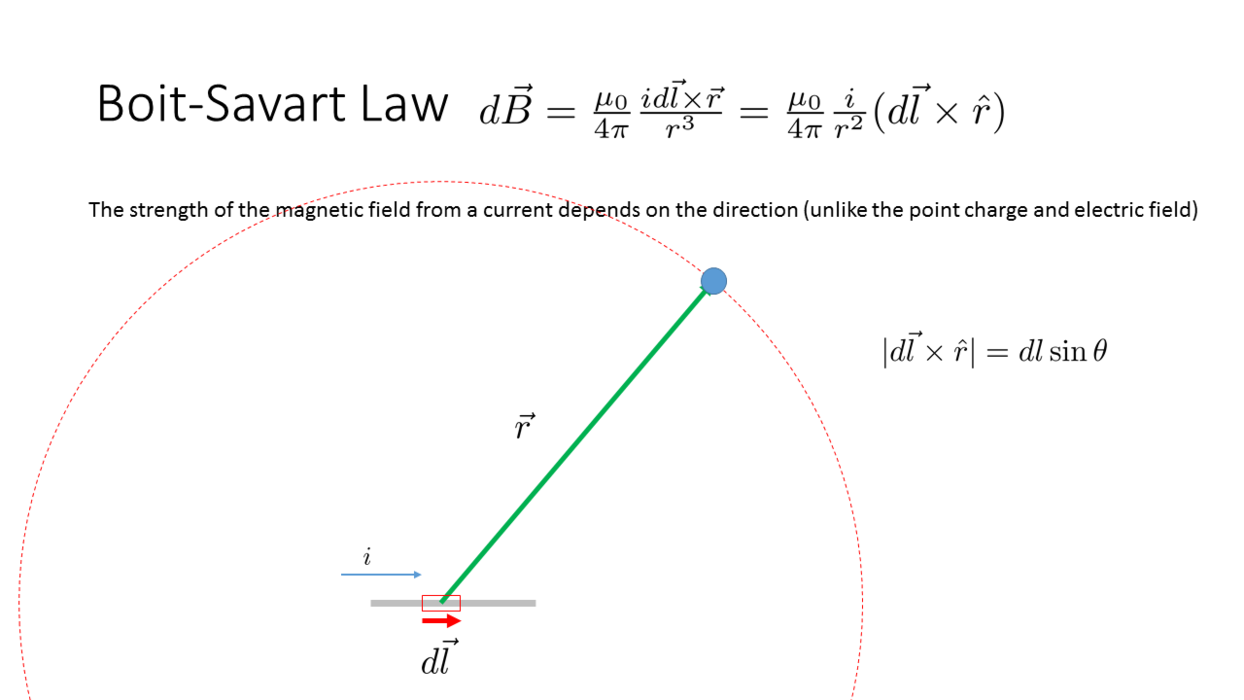
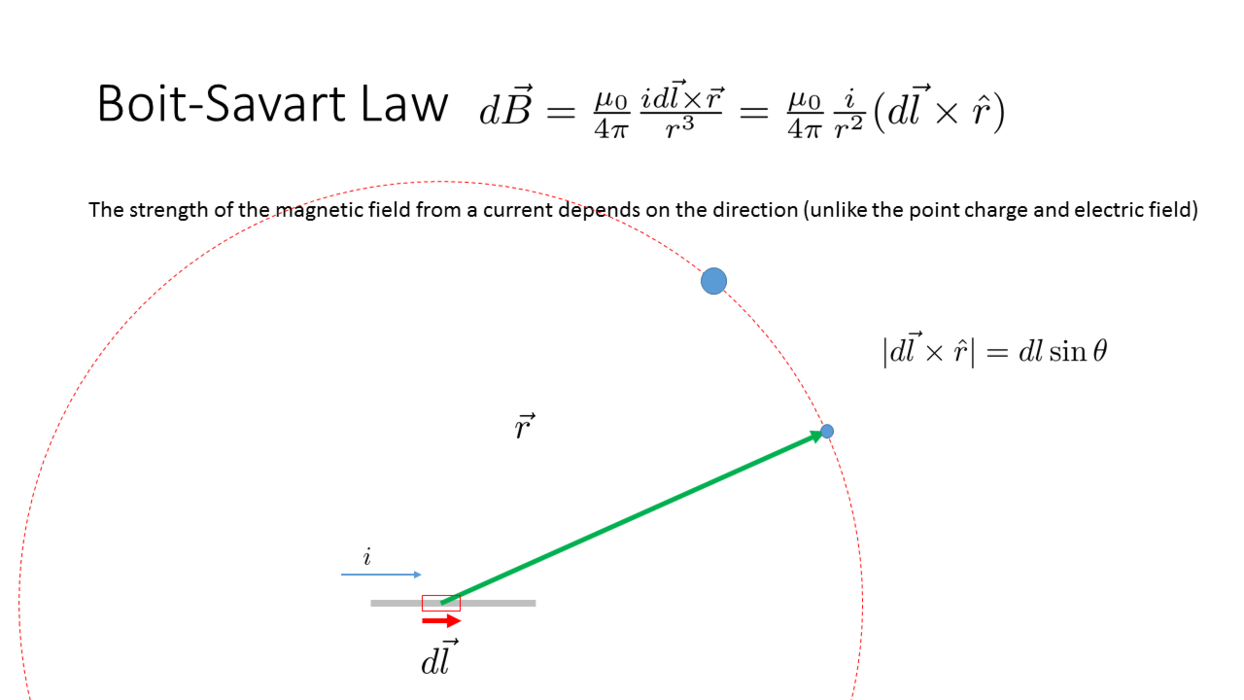
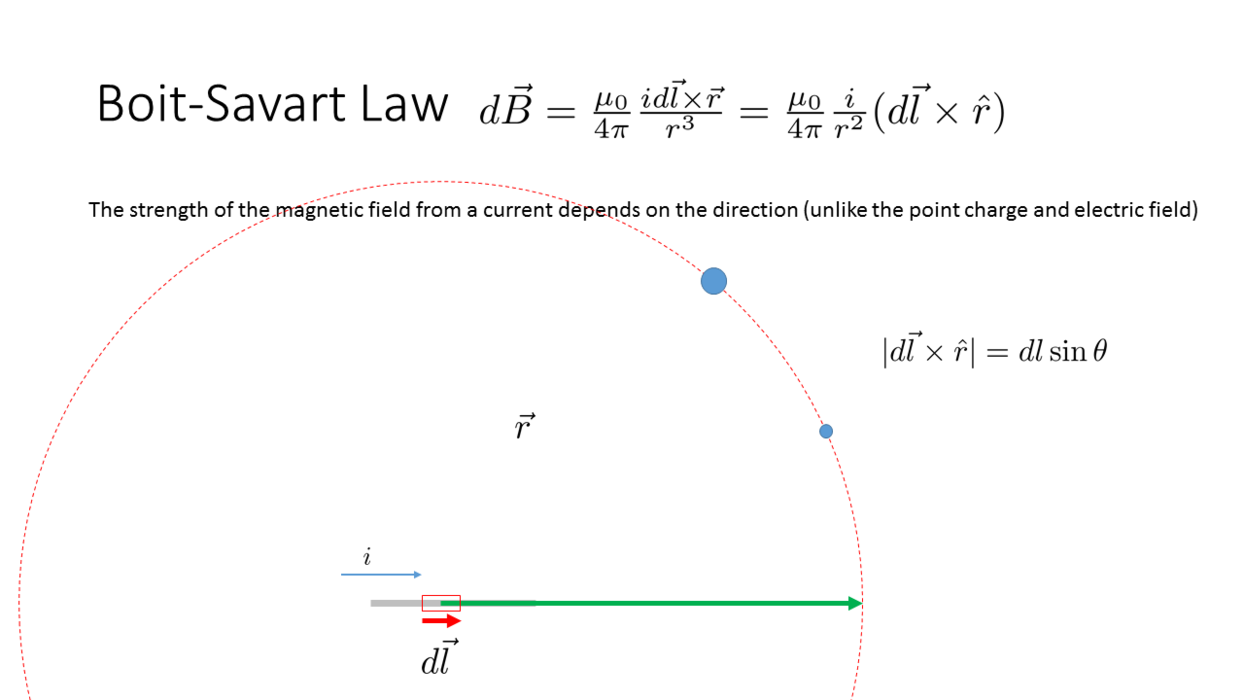
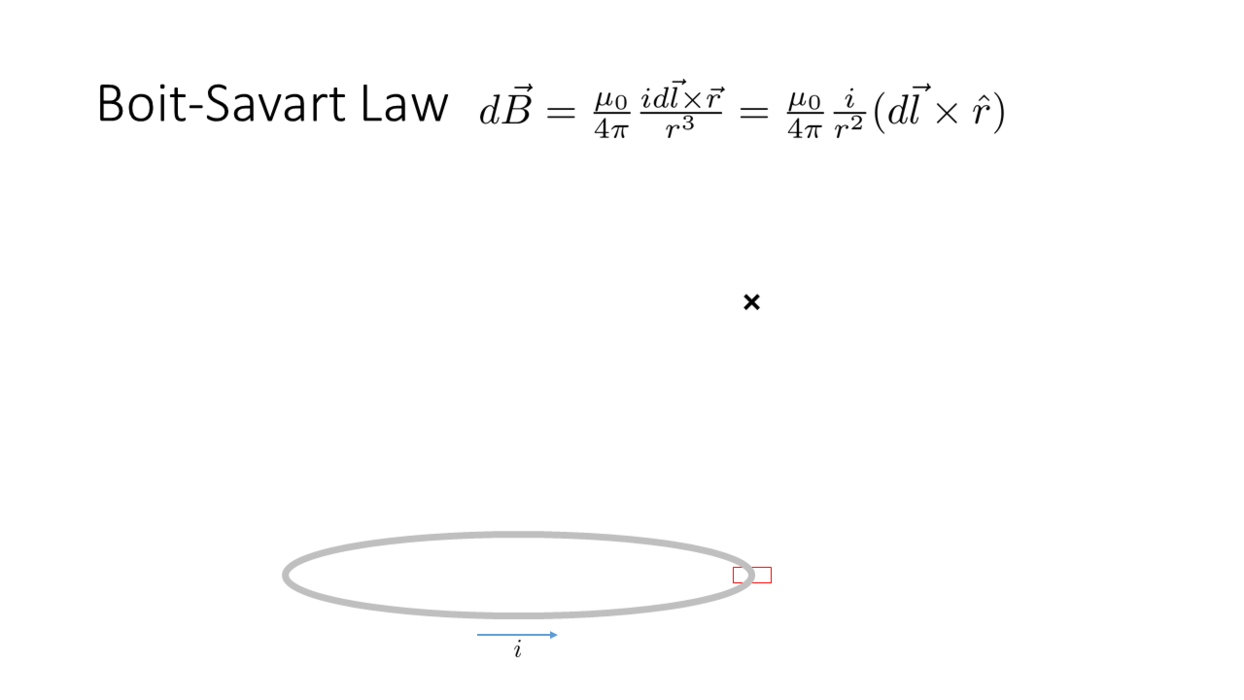
Biot-Savart Law
_
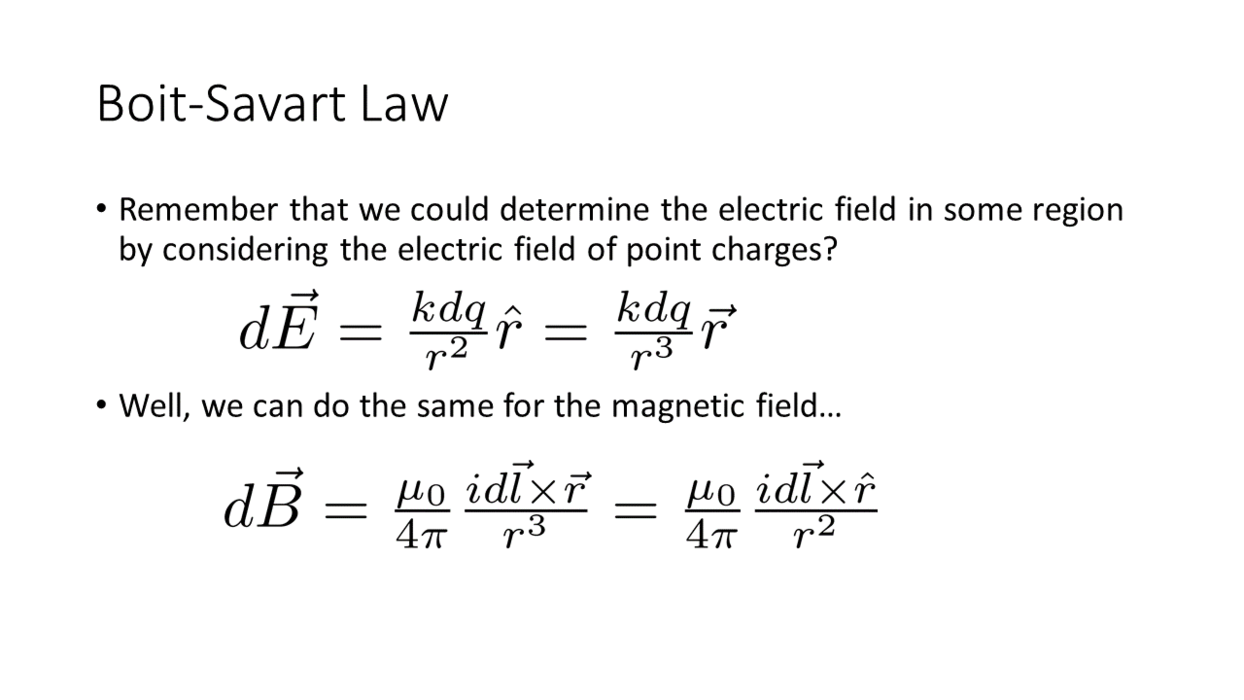
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
_
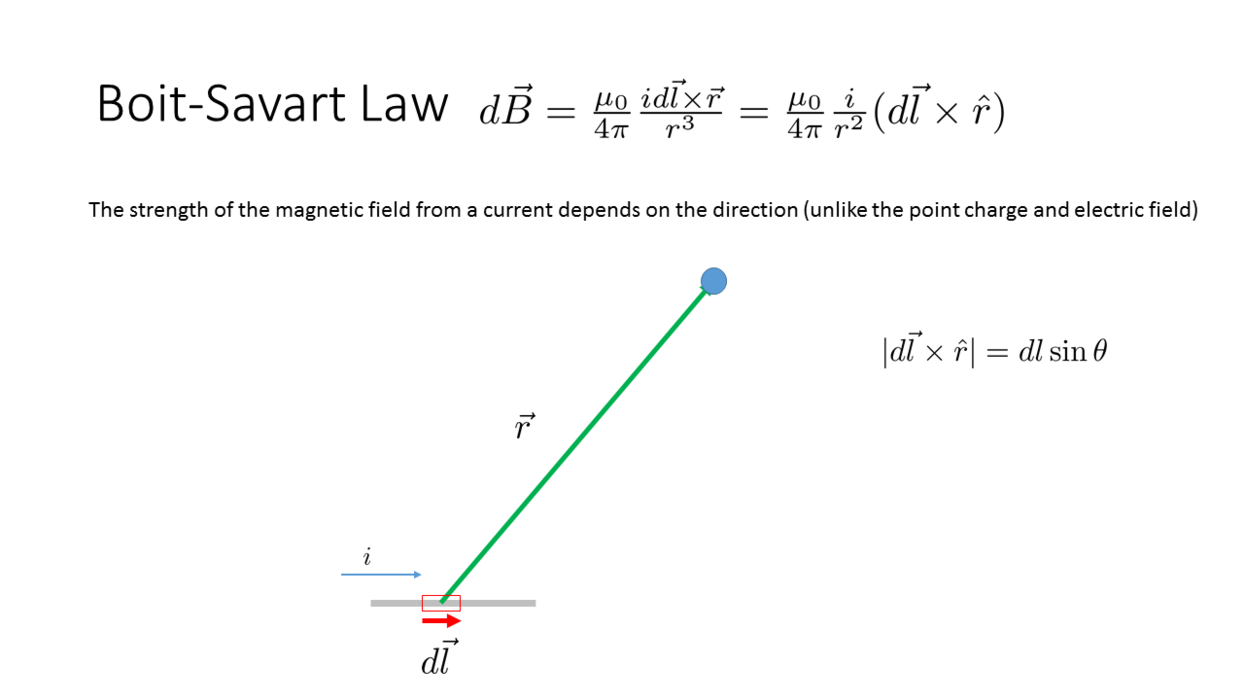
_
_
_
_
_
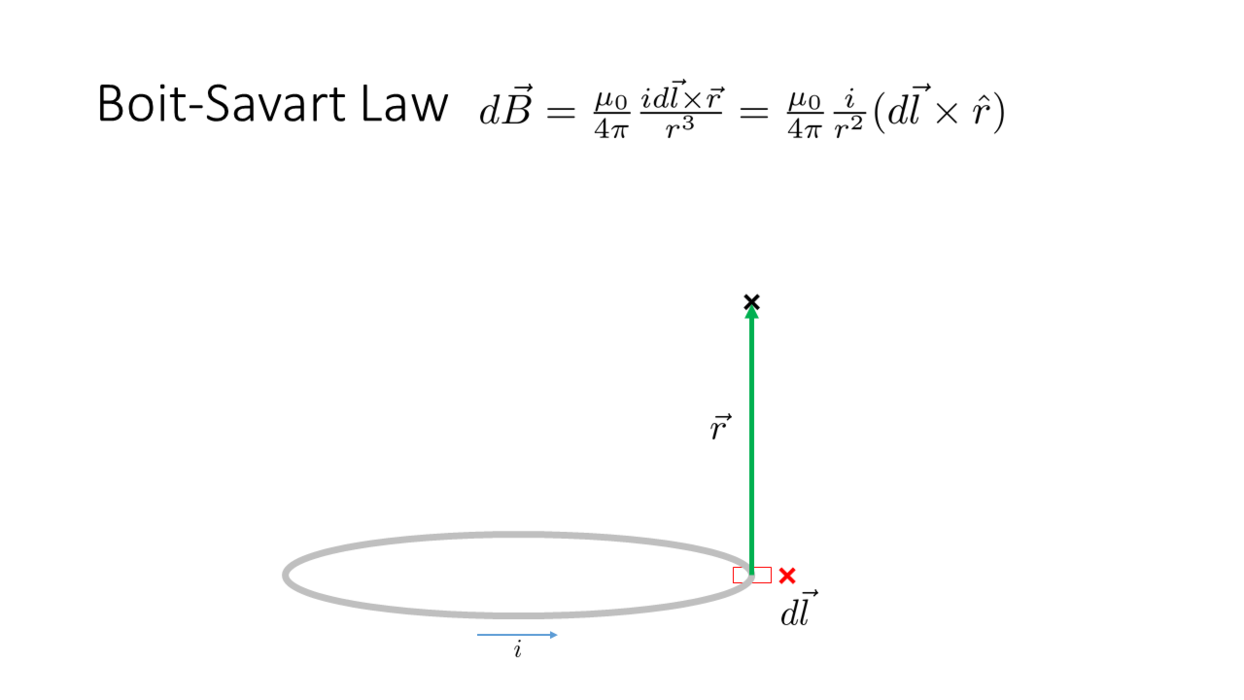
_
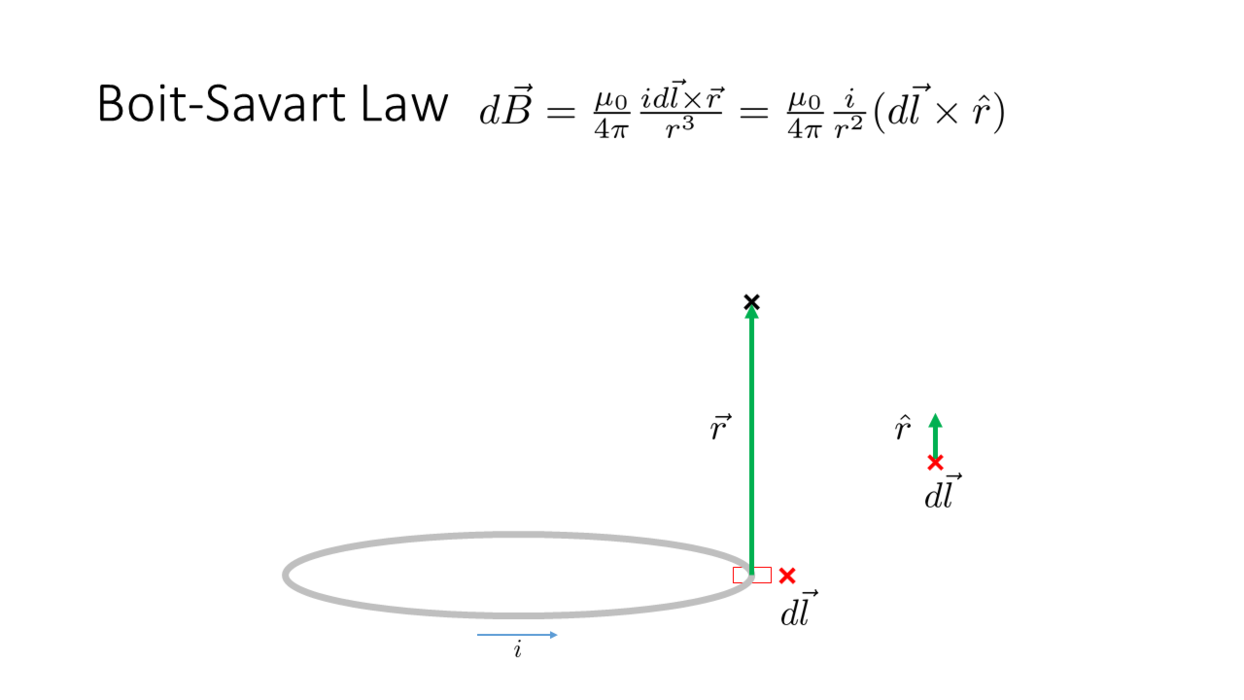
_
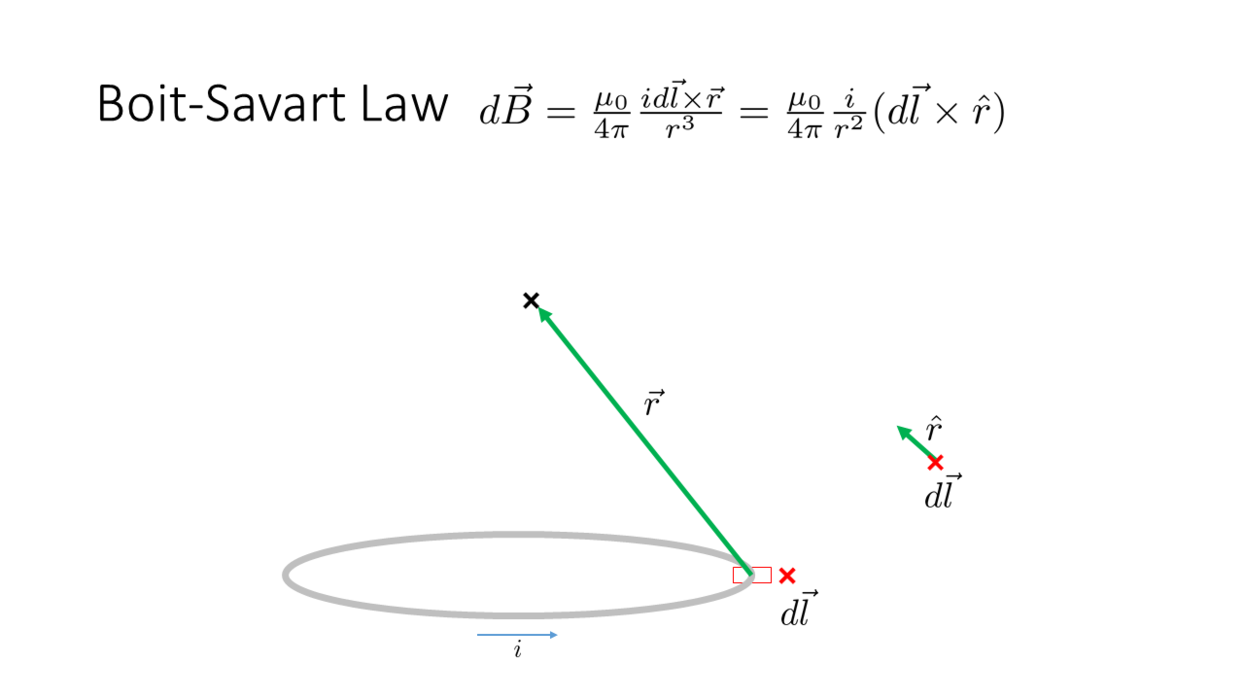
_
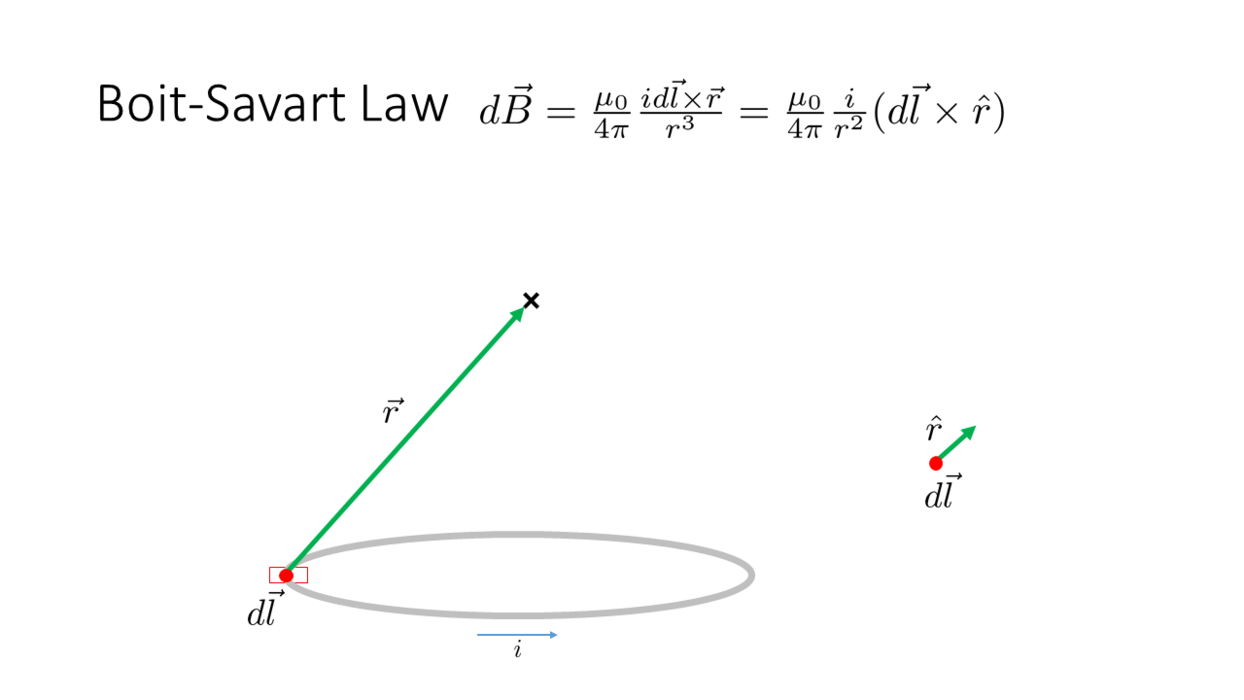
Example
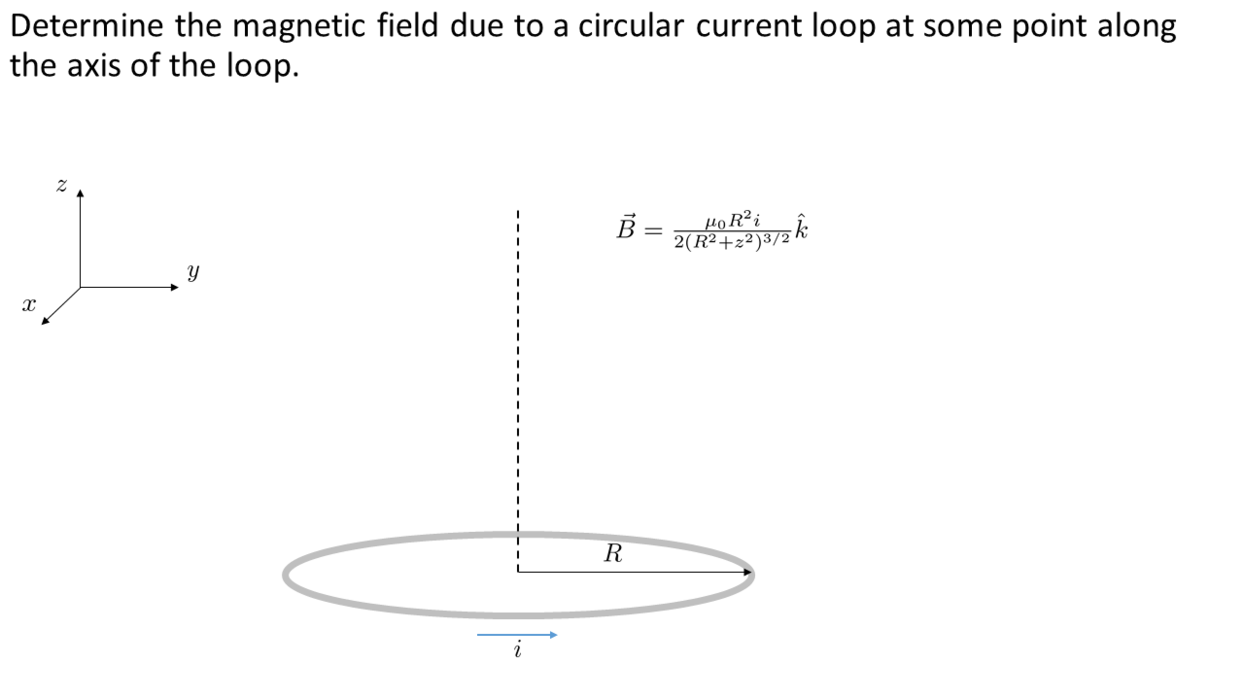
Example
Multiple Sources
- The magnetic fields adds just like the electric field.
- If we know they field from two sources separately, we know the field from the two sources together.
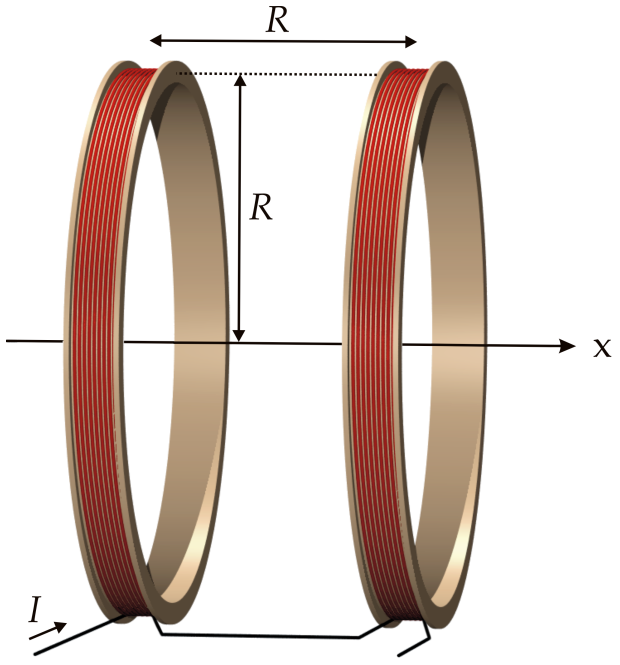
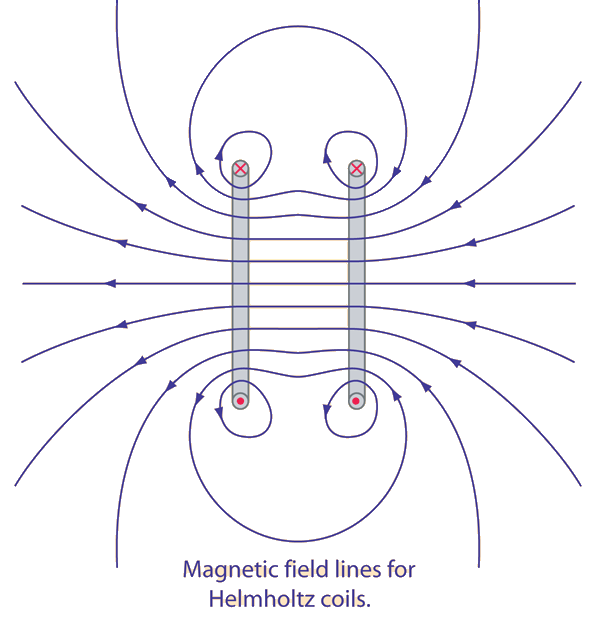
Multiple Sources
- The magnetic fields adds just like the electric field.
- If we know they field from two sources separately, we know the field from the two sources together.

Multiple Sources
- The magnetic fields adds just like the electric field.
- If we know they field from two sources separately, we know the field from the two sources together.

Multiple Sources
- The magnetic fields adds just like the electric field.
- If we know they field from two sources separately, we know the field from the two sources together.
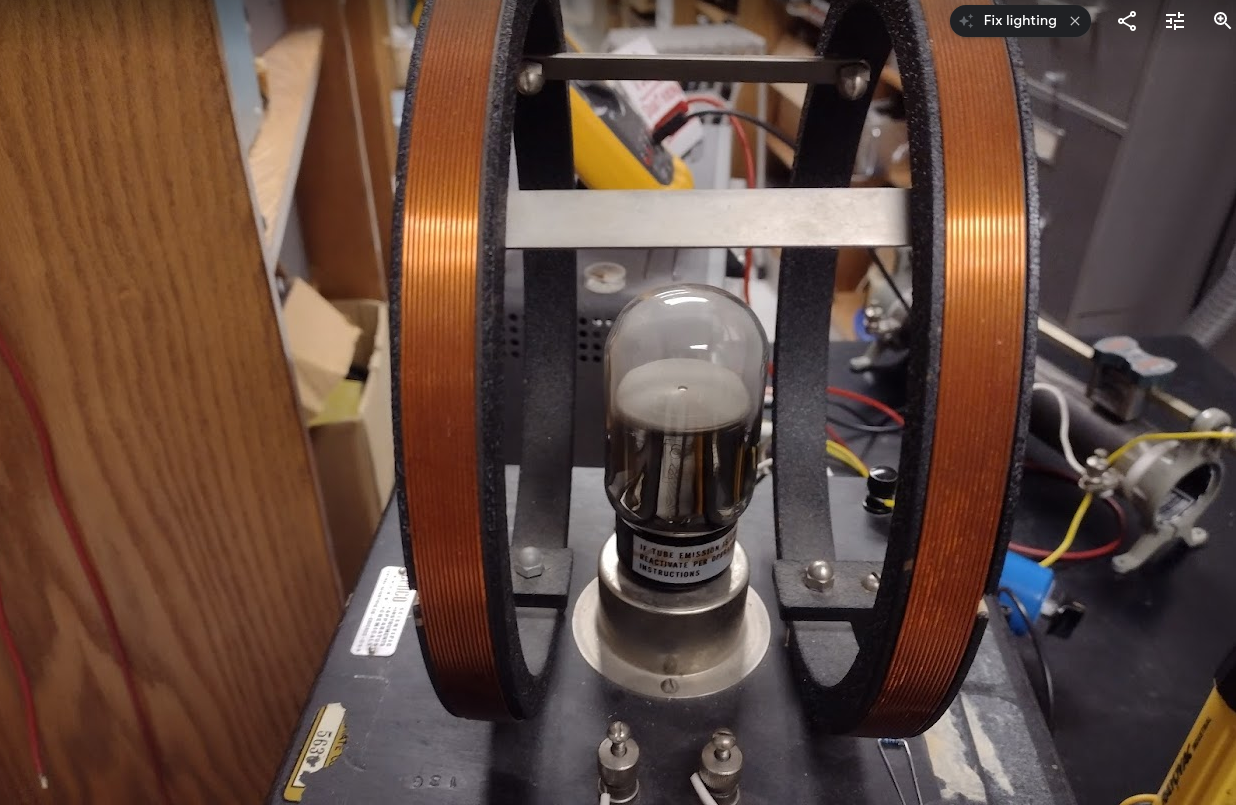
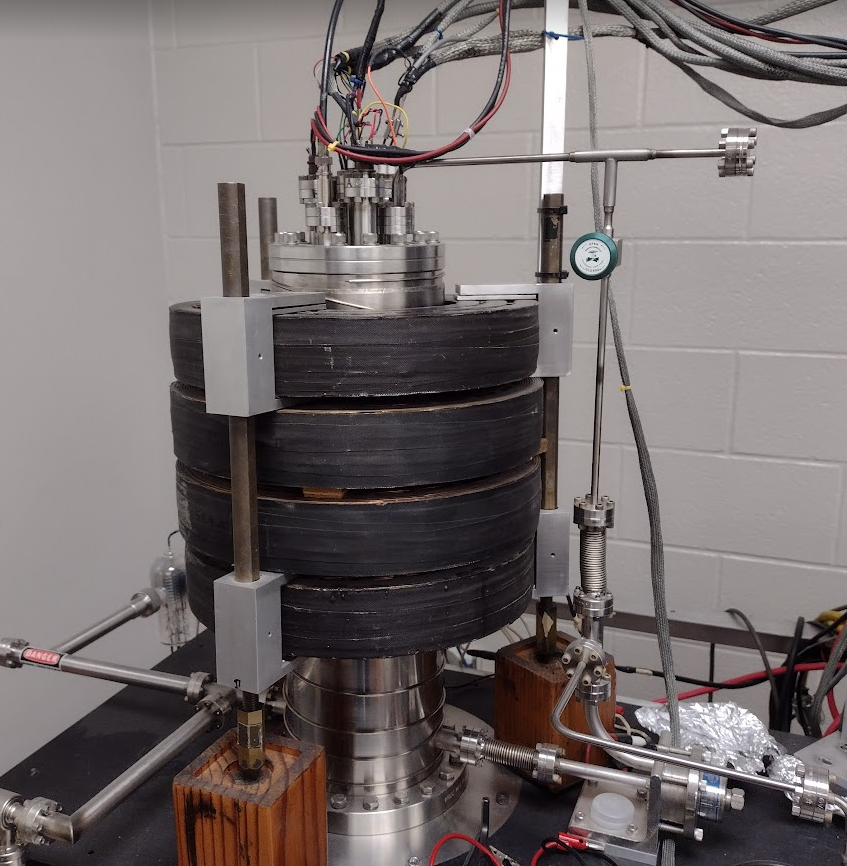
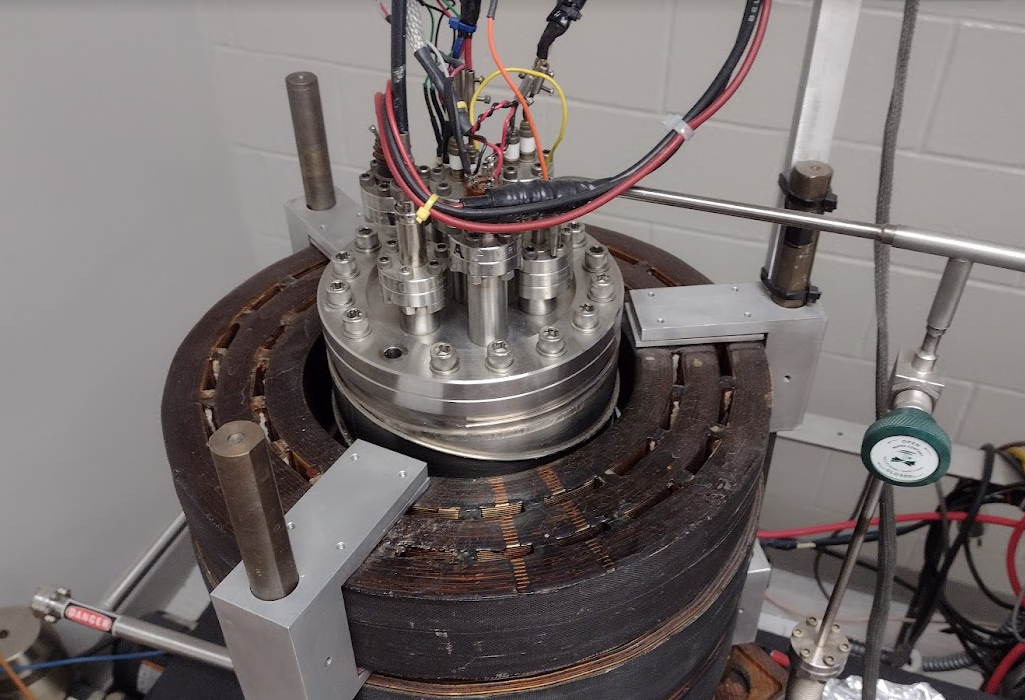
Electromagnets
Example: Finite length, straight current
Determine the magnetic field due to a finite length of wire (length \(L\)), at a distance \(r\) from the wire. 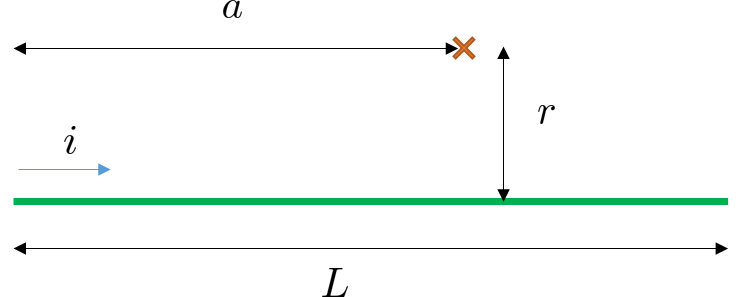
Last Slide
Last Slide
No really, that was the last one.
Last Slide
There is nothing to see here!
Last Slide
Look, I know that the slide count says there are more slides, but there aren’t any more.
Last Slide
Seriously, its just a bunch of Last Slide slides.
Last Slide
This is the last one that says anything funny. You can stop clicking now.
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
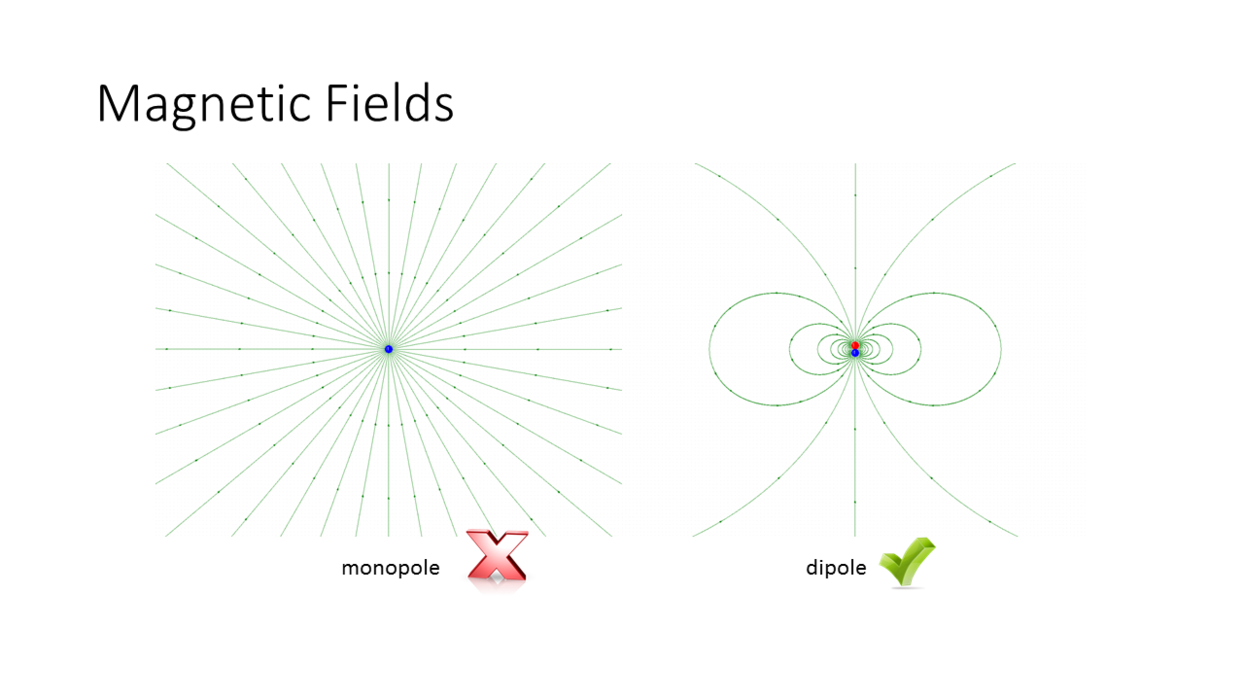
Magnetic Monopoles
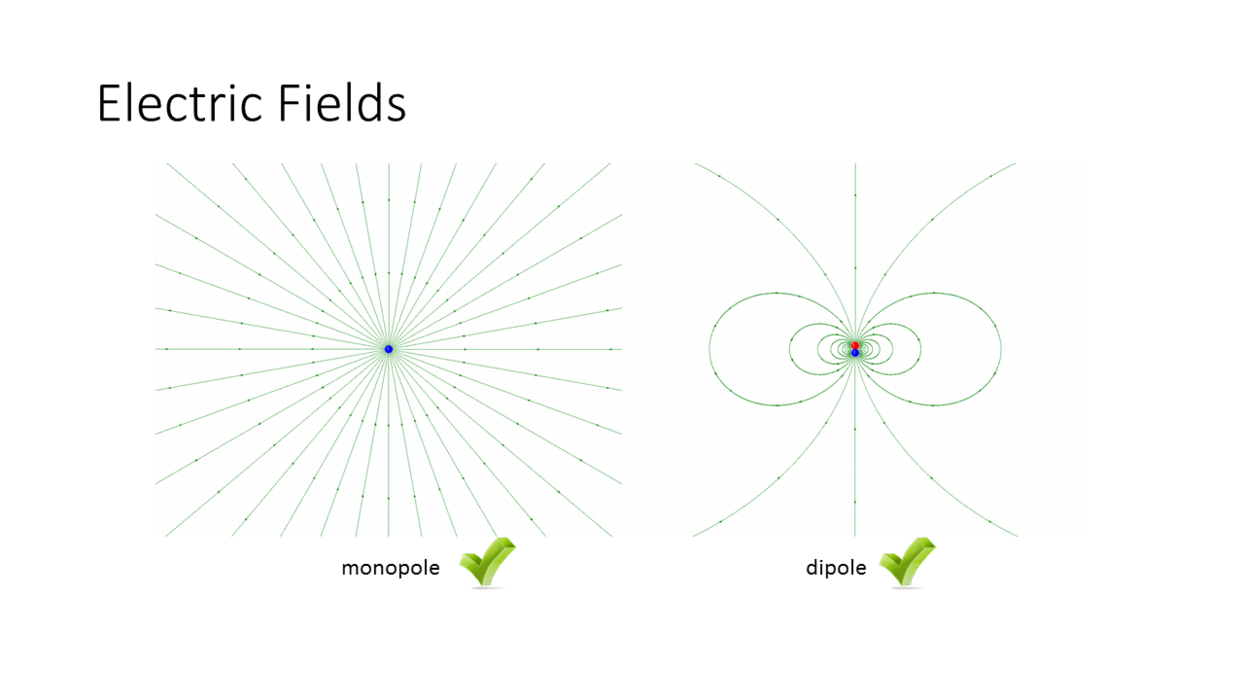
Magnetic Monopoles
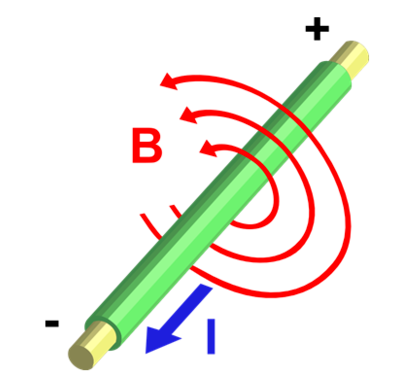
Magnetic field from long straight wire
- The magnetic field lines around a long straight wire will form circular, closed loops around the wire.
- The direction of these lines can be found by the right-hand rule:
- Point thumb in direction of current.
- Figures curl around the wire in the direction of the magnetic field.
- The field strength decreases farther away from the wire:
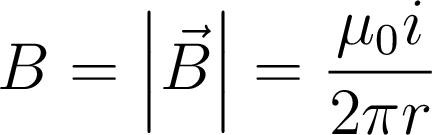 |
 |
| \(\mu_0\) is called the "permiability of free space |
|
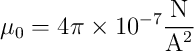 |
|
Right-hand Rules
- We have a new right-hand rule for the direction of a magnetic field produced by current.
- This RHR can be used for current loops as well, but…

_

_