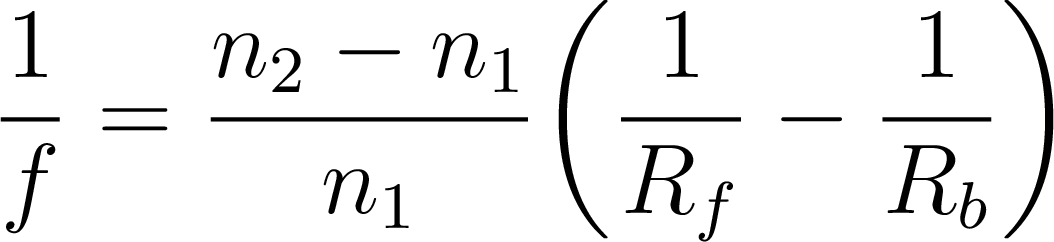Last Updated: Tue Nov 5 03:11:21 PM CST 2024
Geometric Optics
- We model light as rays that propagate through space.
- A light source emits rays of light.
- Surfaces reflect or refract light rays (or absorb) according to the
law of reflection and refraction.
- Optics problems basically become geometry problems.
Reflection and Refraction
Convention
- Incident ray
- Reflected ray
- Refracted ray
- Angle of incidence, reflection, and refraction are all measured with
respect to the surface normal.
Reflection:
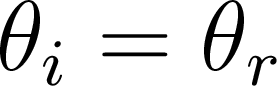
Refraction (Snell’s Law):
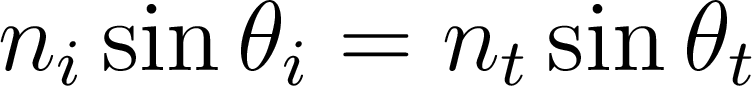
Light Ray Box: Reflection and Refraction
Laser beams travel along straight lines, just like rays. This gives
us a nice way to “see” ray optics.
- Law of reflection
- Law of refraction
Light Ray Box: Total Internal Reflection
If the refracted angle is greater than 90 degrees, then we get
complete reflection.
This is called “total internal reflection”.
Examples: Retro Reflector
Consider a ray of light incident on two mirrors that make a 90 degree
angle.
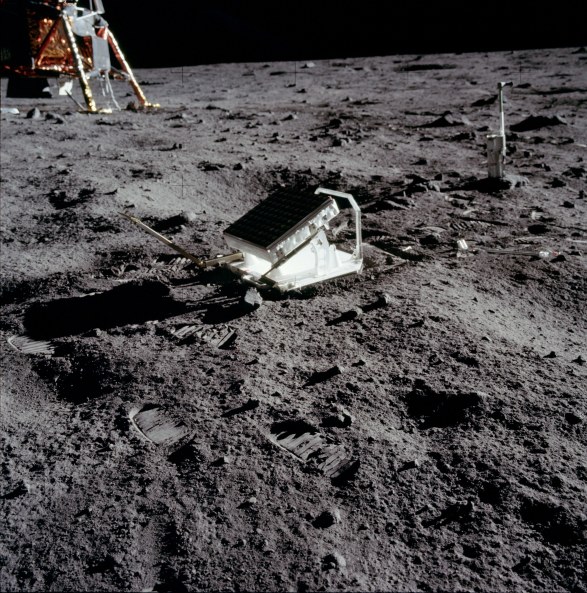
 How far
away is the moon?
How far
away is the moon?
Examples: Depth Perception
If you collect two rays from the same source, you can work out where
the source is at.
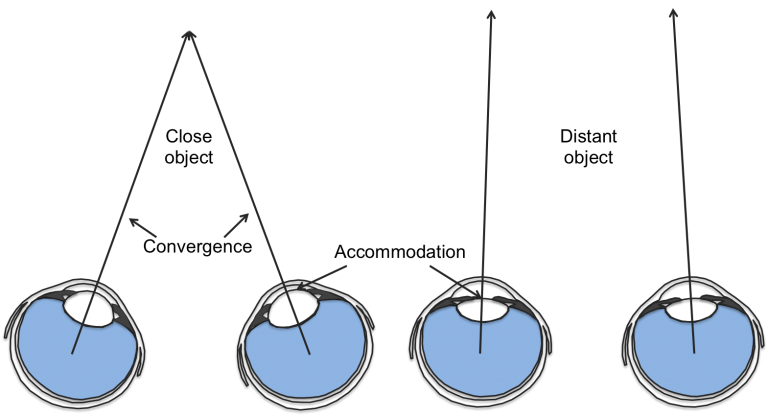
This is an example of triangulation
Examples: Apparent Position and Mirrors
We can determine where an image of an object in a mirror will appear
to be by considering two rays from the object reflected off of the
mirror.
Examples: Apparent Position and Refraction
We can do the same thing for refraction.
- How deep does a fish look if it actually sits a distance \(d\) below the surface of the water?
Small Angle Approximation
We will often find that the small angle approximation greatly
simplifies our algebra.
Small Angle Approximation
When angles are small, we can approximate sine, cosine, and tangent
in terms of the angle directly.
- \(\sin\theta \approx \theta\) (in
radians!)
- \(\cos\theta \approx 1 -
\frac{1}{2}\theta^2\)
- \(\tan\theta \approx \sin\theta \approx
\theta\)
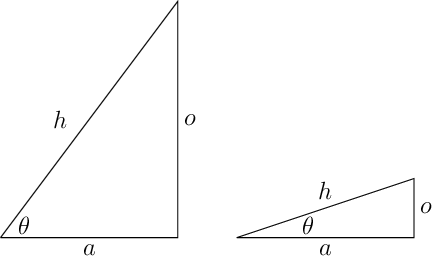
Small Angle Approximation
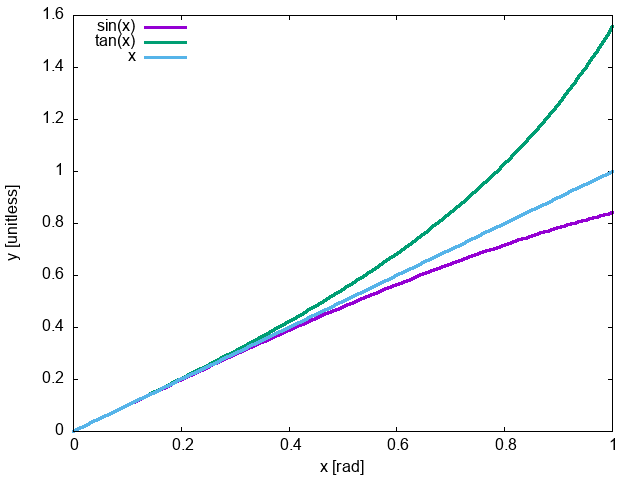
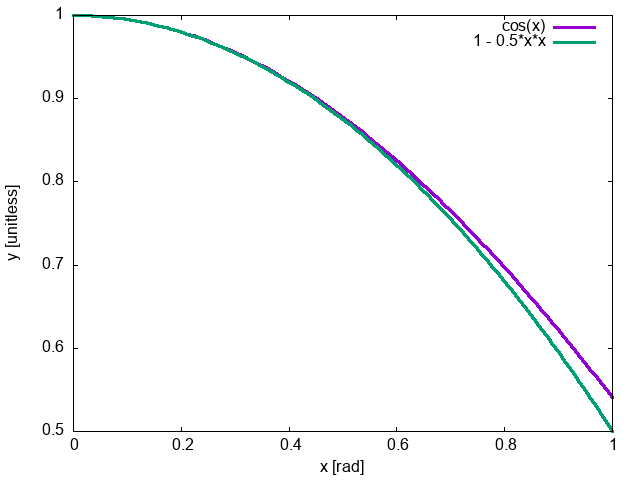
Small Angle Approximation
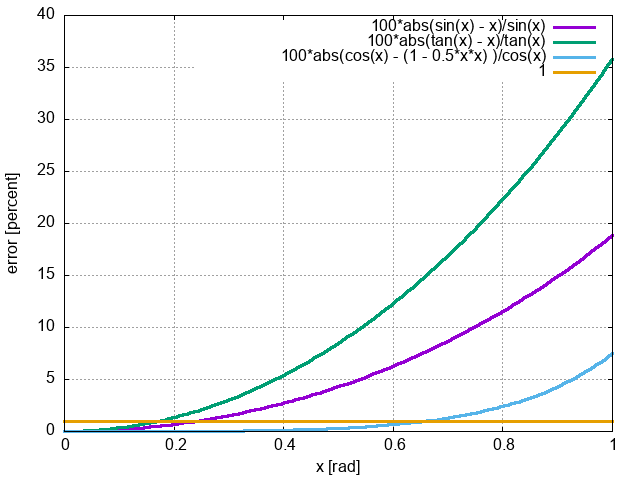
Small Angle Approximation
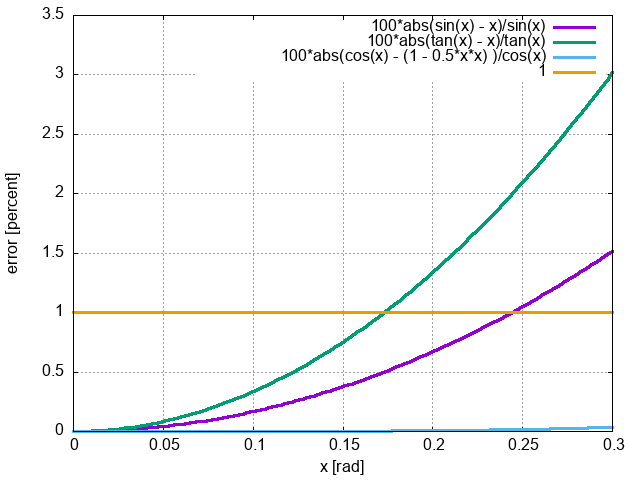
All approximations will have less than a 1% error for angles less
than 0.17 radian, which is about 10 degrees.
Examples: Apparent Position and Refraction
Some objects are not where they appear…

Examples: Apparent Position and Refraction
We can do the same thing for refraction.
- How deep does a fish look if it actually sits a distance \(d\) below the surface of the water?
Examples: Spherical Refractive Surface
A spherical refractive surface will bend light toward a single point,
its focal point.
Example: What is the focal length of a convex spherical surface made
of a material with a higher refractive index than the surrounding
media?

Applications: Lenses
- Take two spherical refractive surfaces and put them together.
- Both the front and back surfaces will refract light.
Lensmaker’s Equation
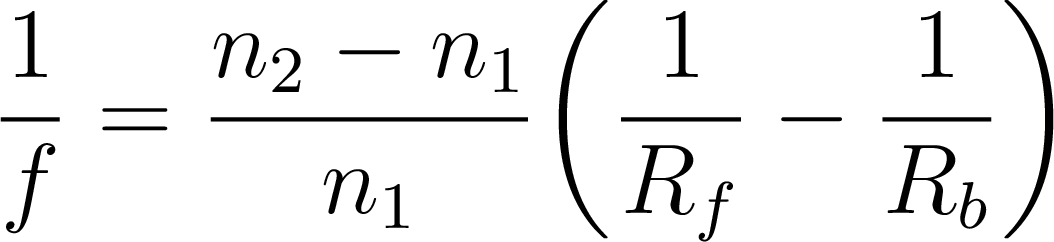
Sign Convention:
- The radius of curvature for each surface may be positive or
negative.
- The RoC is positive if the center of the sphere is on the
“back” side of the lens (where the light rays are going).
- The RoC is negative if the center of the sphere is on the
“front” side of the lens (away from where the light rays are
going).

Applications: Optical Fiber
Total internal reflection is used to transmit light through flexible
glass rods (light wires)
For example, consider a glass rod with a refractive index of 1.5.
What is the “Acceptance Angle”?


Dispersion
Different colors refract different amounts.

This is called “dispersion”.
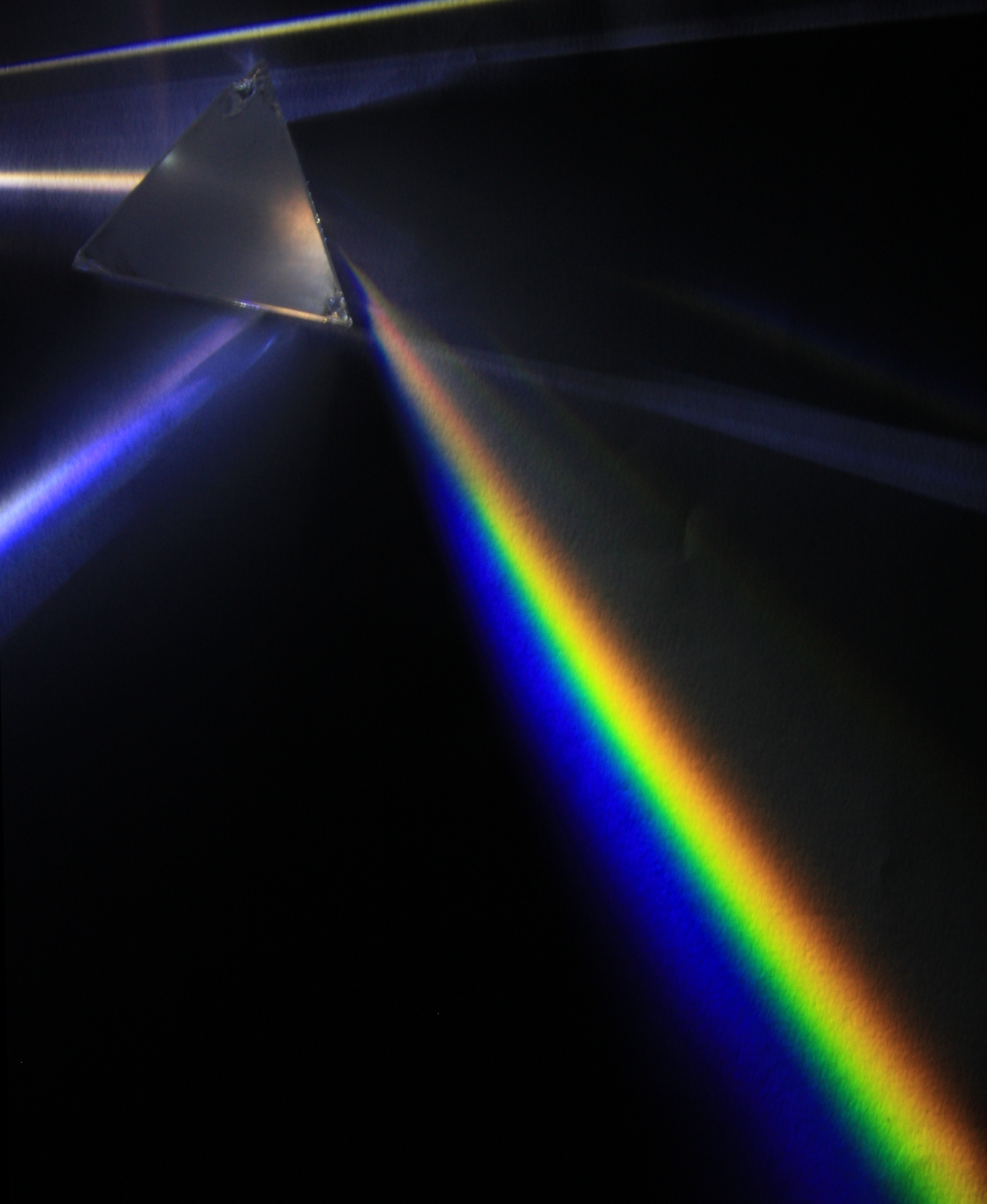

Dispersion
- Light is a wave, so it has a wavelength.
- Our brain interprets different wavelengths of light as different
colors

- The refractive index of most materials depends on its wavelength,
i.e. color

Applications: Prism
- What is the angular separation of red and blue light emerging from a
prism?
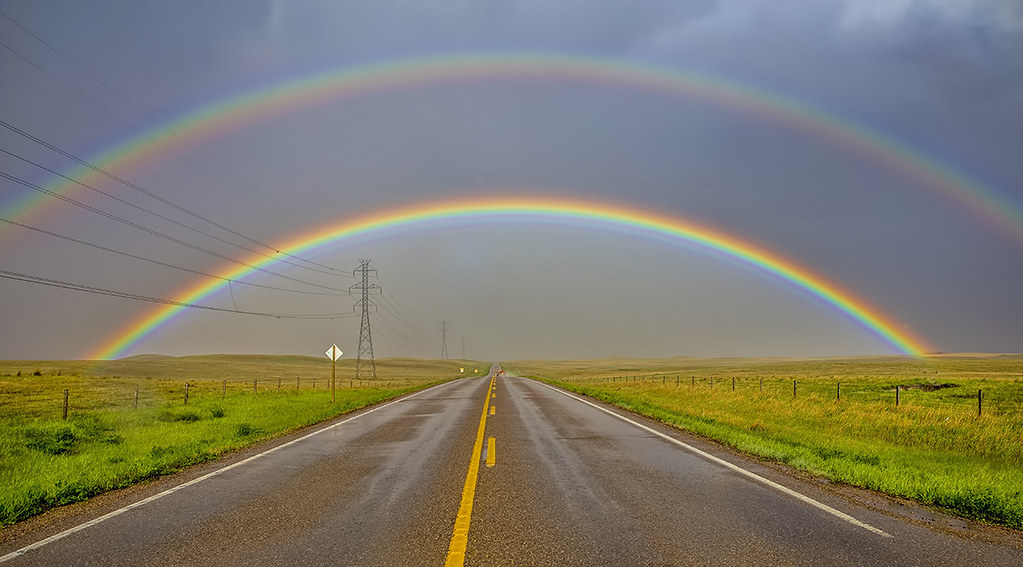
Applications: Rainbows
Water droplets can refract and reflect light rays back toward the
Sun


Applications: Higher-order Rainbows
More than one rainbow can appear. These are called Higher-order.

Applications: Spherical Mirrors
- Mirrors reflect light rays.
- Mirrors can be shaped to reflect light rays to (or away from) a
single point.
Collimating Light
The principle of ray reversal says that for any path that a ray can
take through an optical system, the reverse path is also possible.
For Example
- A lens will bend parallel rays to the focal point.
- A lens will bend rays coming from the focal point to parallel.


Fresnel Lens
What if we needed a lens with a big diameter?
Aberrations
- Not all lenses will bring all rays to the same points.
- Since the refractive index depends on color, different colors will
not be sent to the same points.
- This imperfect ability to focus all rays is called
“aberration”.
- There are various types:
- Some of these can be removed, some cannot.


Last Slide
Last Slide
No really, that was the last one.
Last Slide
There is nothing to see here!
Last Slide
Look, I know that the slide count says there are more slides, but
there aren’t any more.
Last Slide
Seriously, its just a bunch of Last Slide slides.
Last Slide
This is the last one that says anything funny. You can stop clicking
now.
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
Last Slide
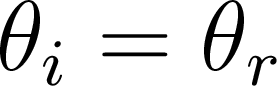
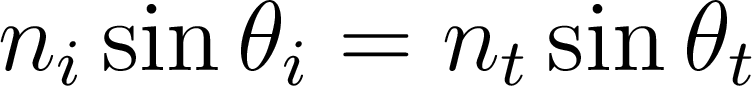
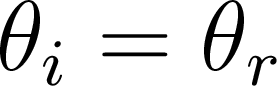
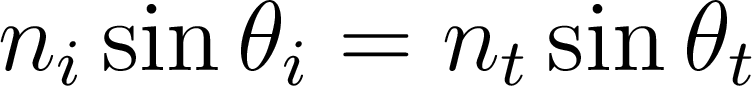

 How far
away is the moon?
How far
away is the moon?