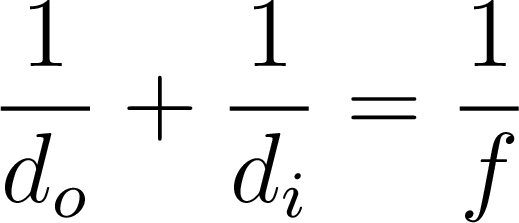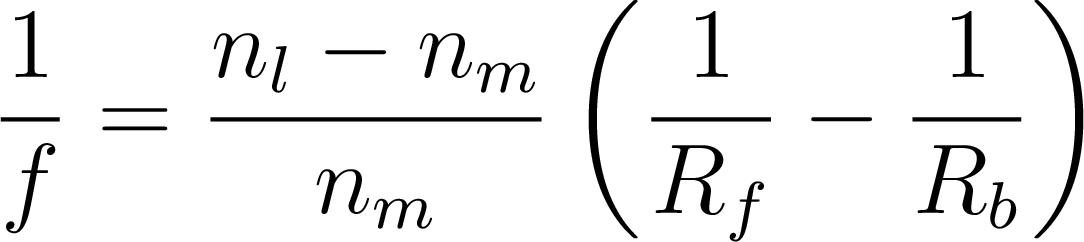Module 12
Last Updated: Thu Nov 21 12:01:11 PM CST 2024
_
_
_
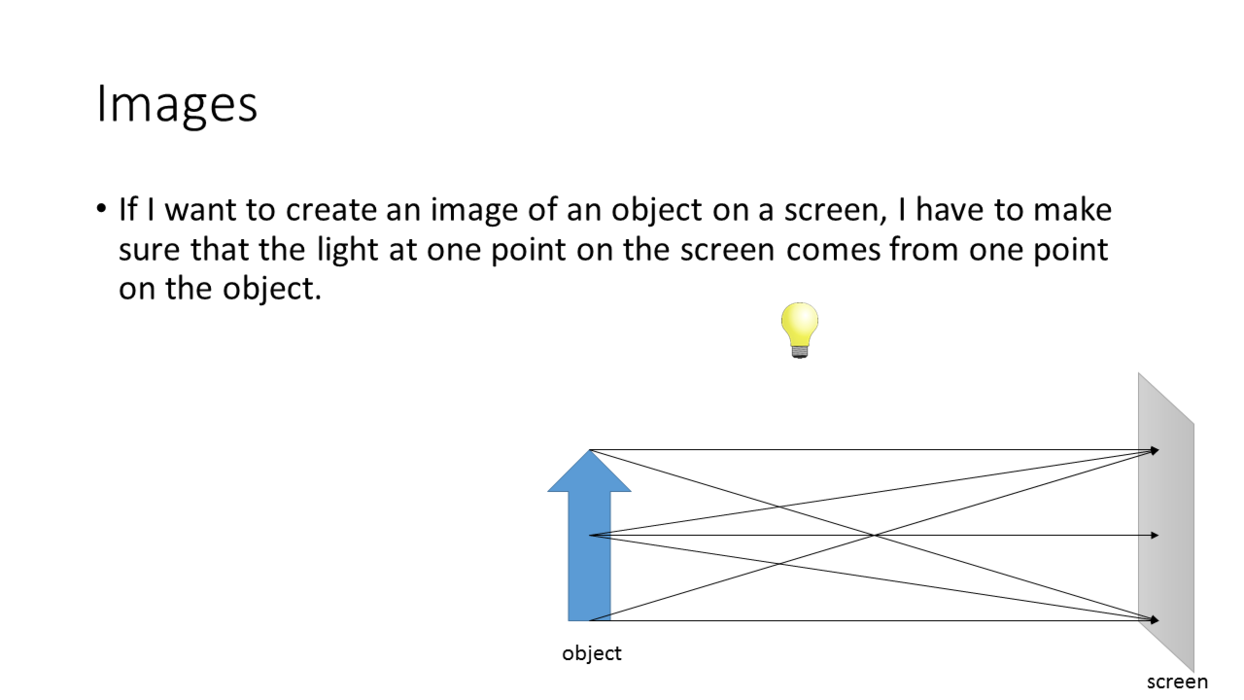
_
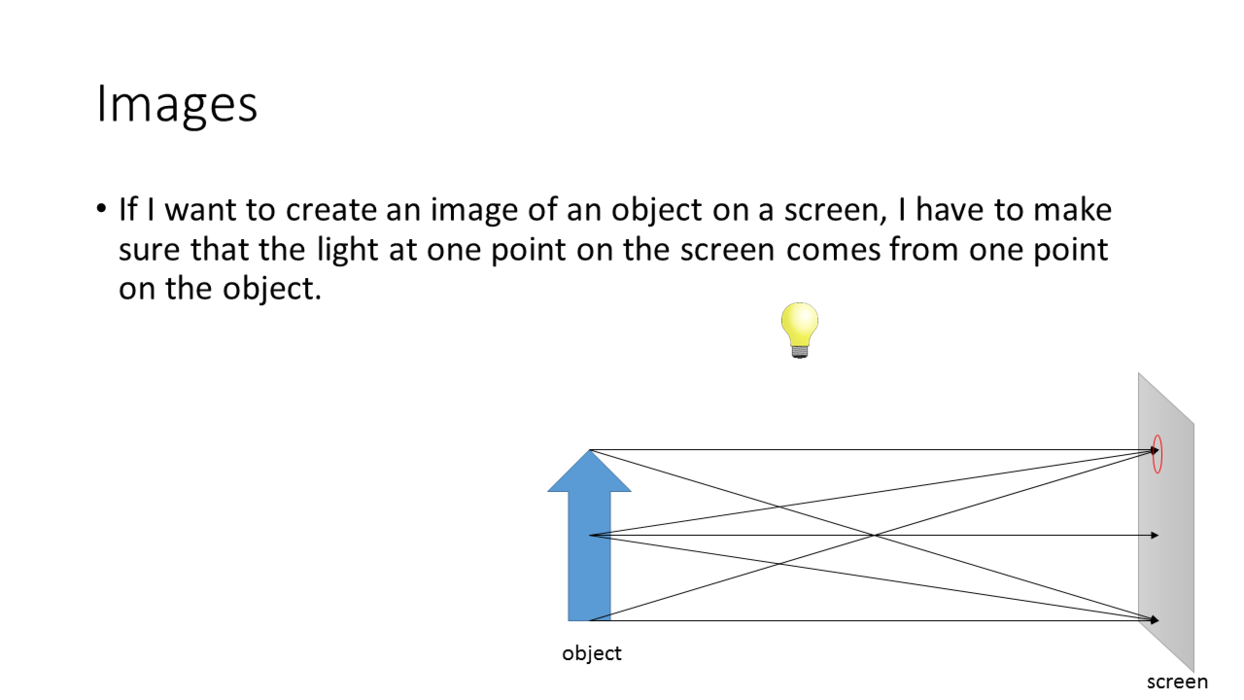
_
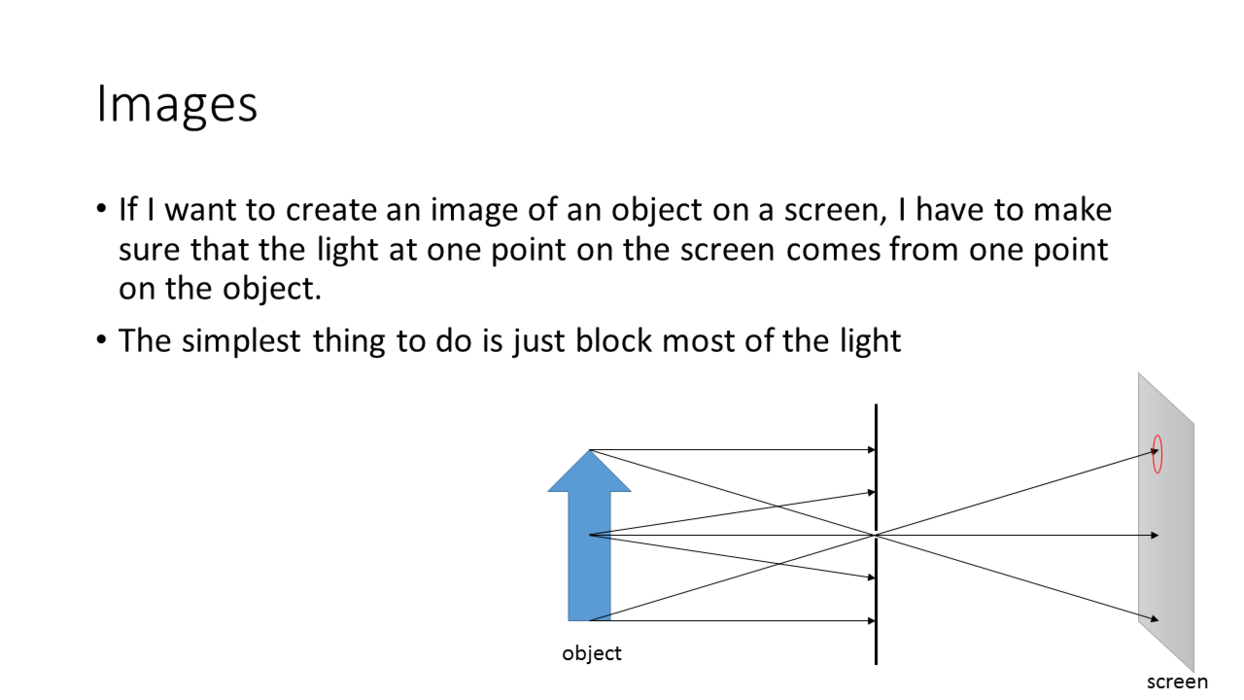
_
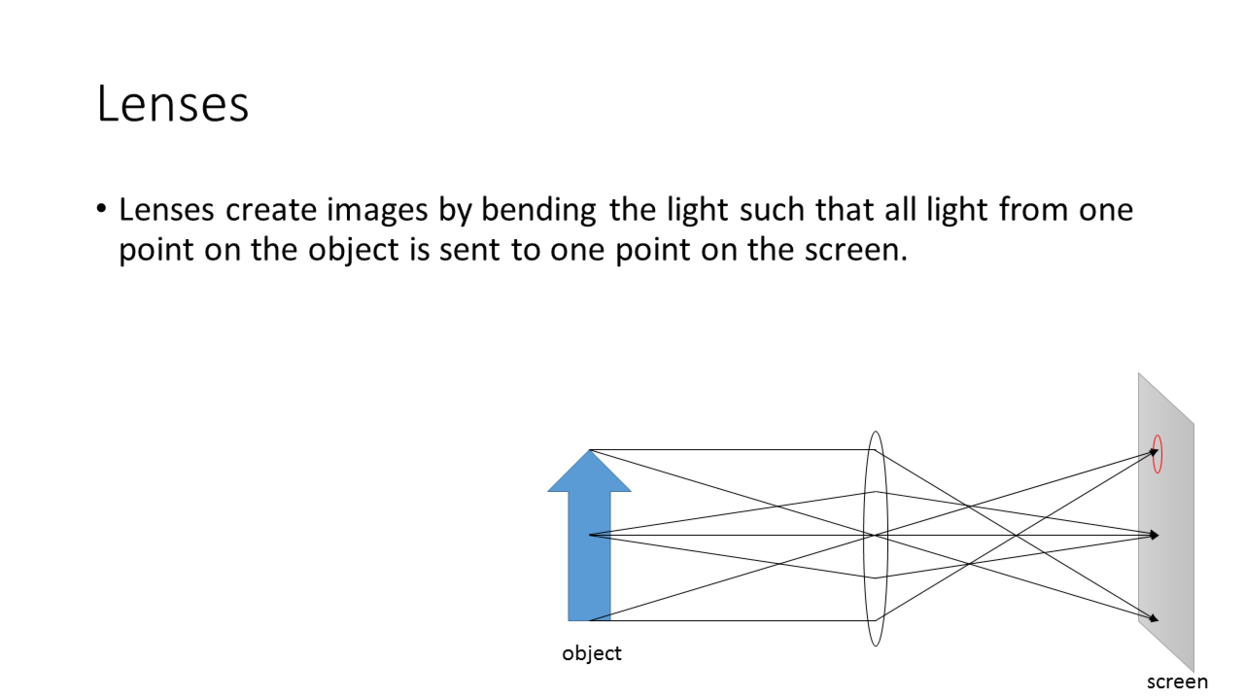
Demo
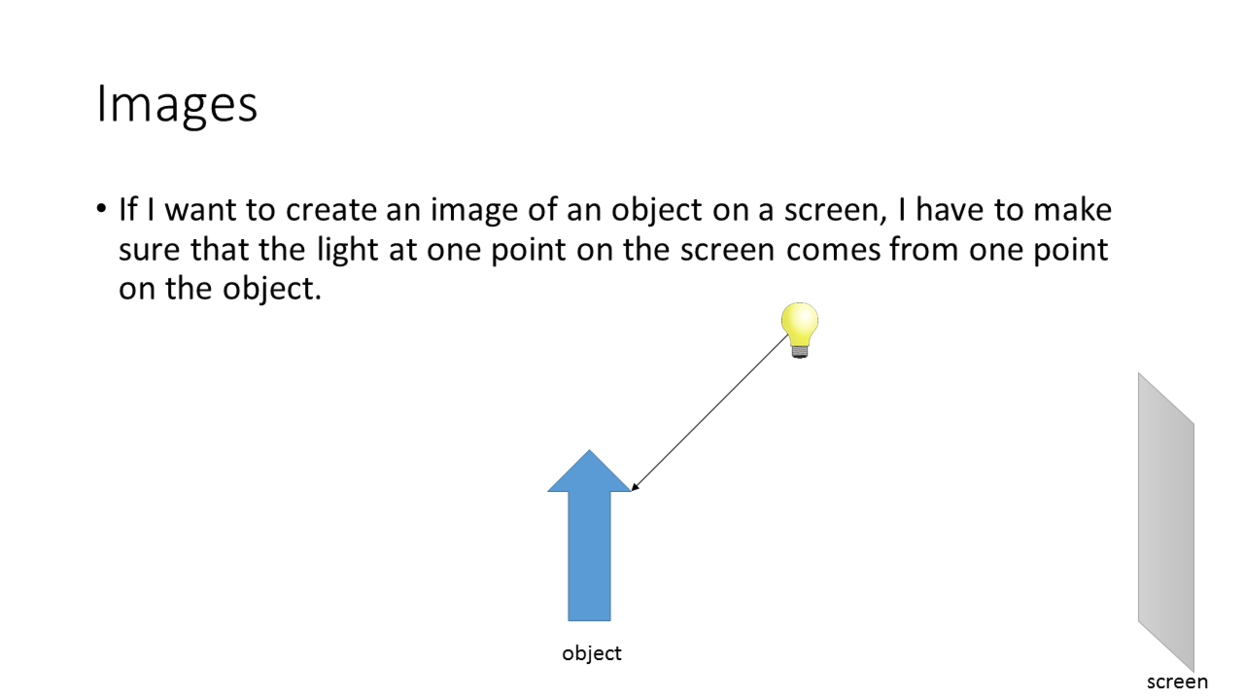
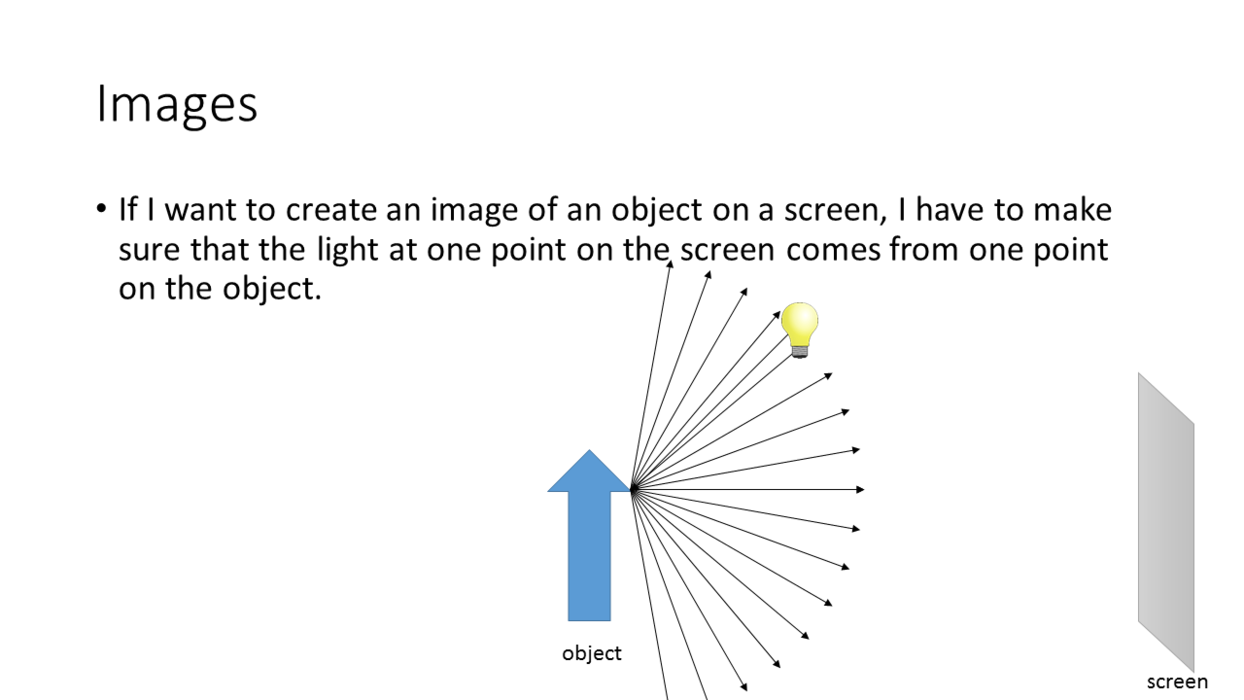
We can form an image of an object on a
screen with a single lens. But:
- The lens must be convex.
- The lens must be the right distance from the screen.
Ray Diagrams : Lenses
We can trace rays of light through a lens to determine where an image
will be formed.
- Rays parallel to the lens axis go through (or extend to) the focal
point.
- Rays passing through (or extending to) the focal point leave the
lens parallel to the lens axis.
- Rays going through the center of the lens are not bent.
Ray Diagrams : Examples
Draw a ray diagram for the following scenarios:
- An object placed far away from a convex lens.
- An object placed near the focal point (but outside) of a convex
lens.
- An object placed inside the focal point of a convex lens.
- An object placed at the focal point of a convex lens.
- An object placed far away from a concave lens.
- An object placed near the focal point (but outside) of a concave
lens.
- An object placed outside the focal point of a concave lens.
- An object placed inside the focal point of a concave lens.
- An object placed at the focal point of a concave lens.
Virtual Images
Virtual images are images that cannot be projected onto a screen.
They can still be imaged though.
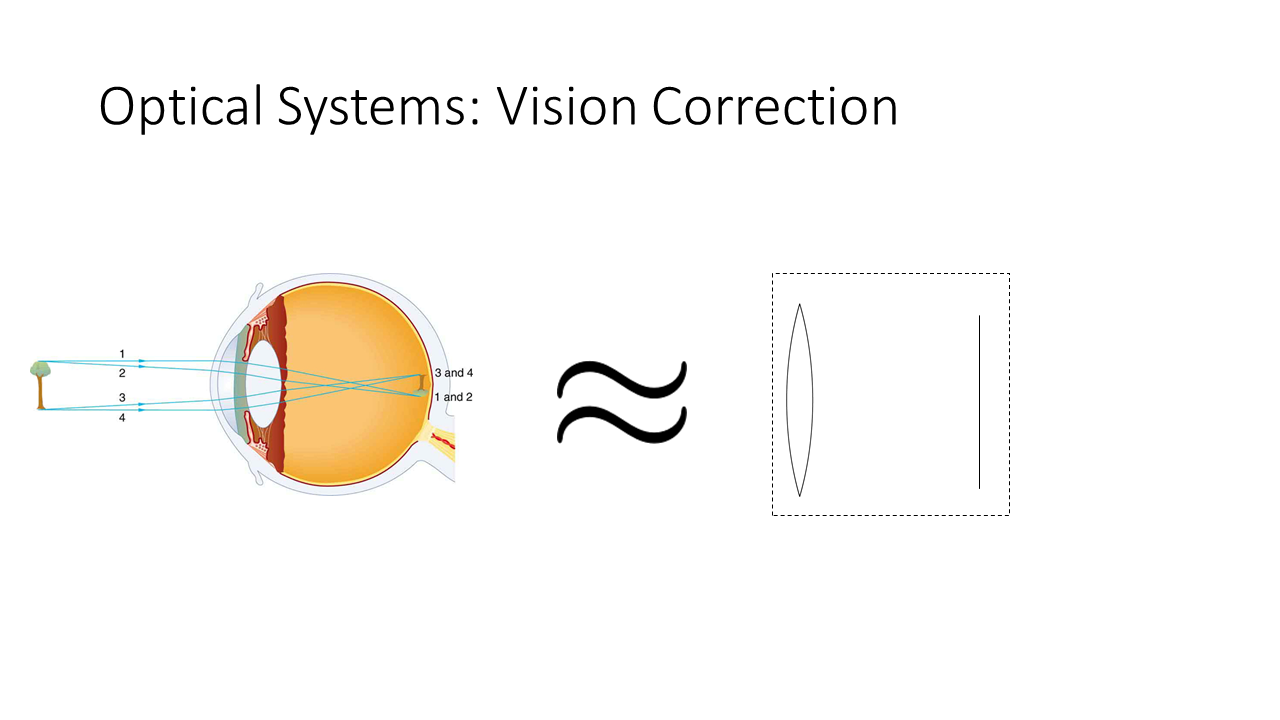
Seeing Images
Our eye is an optical system that creates images of objects on the
retina.
We can see virtual images.
Ray Diagrams : Mirrors
- Rays parallel to the mirror axis go through (or extend to) the focal
point.
- Rays passing through (or extending to) the focal point leave the
mirror parallel to the mirror axis.
- Rays incident and reflected rays at the center of the mirror make
the same angle with the mirror axis.
Ray Diagrams : Examples
Draw a ray diagram for the following scenarios:
- An object placed far away from a convex mirror.
- An object placed near the focal point (but outside) of a convex
mirror.
- An object placed inside the focal point of a convex mirror.
- An object placed at the focal point of a convex mirror.
- An object placed far away from a concave mirror.
- An object placed near the focal point (but outside) of a concave
mirror.
- An object placed outside the focal point of a concave mirror.
- An object placed inside the focal point of a concave mirror.
- An object placed at the focal point of a concave mirror.
Rays
Image Equation
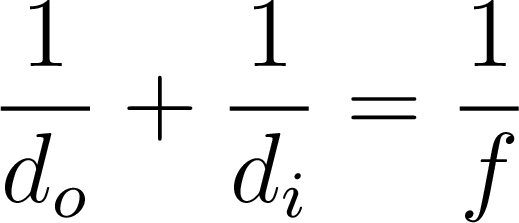
Sign Convention
- radius of curvature: \(R\)
- positive when center of sphere is on the side rays
go to.
- negative when center of sphere is on the side rays
come from.
- focal length: \(f\)
- positive when parallel rays pass
through the focal point.
- negative when parallel rays diverge away
from the focal point.
- object distance: \(d_o\)
- positive when on the side rays come
from.
- negative when on the side rays go
to.
- image distance: \(d_i\)
- positive when on the side rays go
to.
- negative when on the side rays come
from.
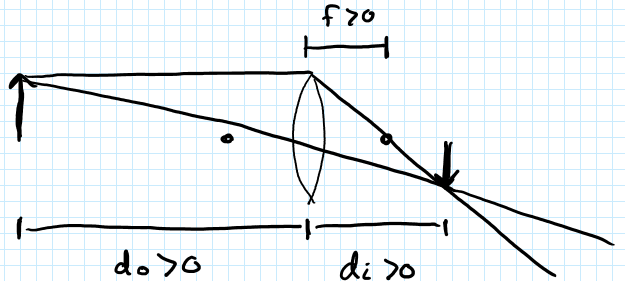
Sign Convention
Consider this “standard scenario”
Examples
- An object is placed 20 cm in front of a 15-cm convex lens. Where is
the image formed?
- An object is placed 15 cm in front of a 20-cm convex lens. Where is
the image formed?
- An object is placed 20 cm in front of a 15-cm concave lens. Where is
the image formed?
- An object is placed 15 cm in front of a 20-cm concave lens. Where is
the image formed?
Magnification
- The image and object, in general, are not the same size. The
magnification is the ratio of the image size to object size.
- This turns out to be the same as the ratio of the image distance to
the object distance
\(m = \frac{h_i}{h_o} =
-\frac{d_i}{d_0}\)
Angular Magnification
The apparent size of an object or image is not how big it actually
is, but how much of our field of view it spans.
\[
\alpha = 2\tan^{-1}\left(\frac{h}{2r} \right) \approx \frac{h}{r}
\]
Multiple lenses/mirrors
- When we have multiple lenses, each lens images the image created by
the lens before it.
- So the image of each lens becomes the object of the next lens.
Example
An object is placed 30 cm in front of a 10 cm convex lens. A 20 cm
concave lens is placed 20 cm behind the convex lens.
- Where will the final image be formed?
- What will the magnification of the final image be?
- Will the final image be upright or inverted?
Negative Object Distance
- If an object is behind a lens or mirror, it has a negative
object distance.
- This isn’t possible with a single lens/mirror, but it is with
multiple lenses/mirrors
- We use the exact same same formula, just keep track of the
sign.
Example
An object is placed 20 cm in front of a 15 cm convex lens. A second
convex lens is placed 10 cm behind the first. The second lens has a
focal length of 20 cm.
- Where will the final image be formed?
- What will the magnification of the final image be?
- Will the final image be upright or inverted?
Nearsightedness and Farsightedness
- Nearsighted-ness is caused by the cornea being too sharply curved.
- This means that the focal length of the cornea alone, is too far in
front of the retina.
- Farsightedness is caused by the lens not being able to compress
enough.
- This means that the focal length cannot be moved far enough away
from the retina.
Example
So, a person with near-sighted vision has a far point that is not at
infinity. But, their near point is closer!
Lens Maker’s Equation
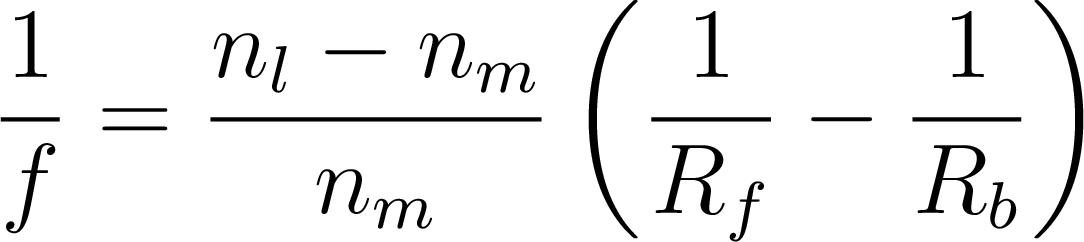
- \(f\) focal length of the lens
- \(n_l\) refractive index of lens
material
- \(n_m\) refractive index of media
(surrounding material)
- \(R_f\) radius of curvature of the
front surface
- \(R_b\) radius of curvature of the
back surface
- Remember: we have a sign convention for the radius of
curvature!

Optical Instruments
- Telescopes and microscopes create magnified images of things that
are small (visually).
- Remember angular magnification vs linear magnification