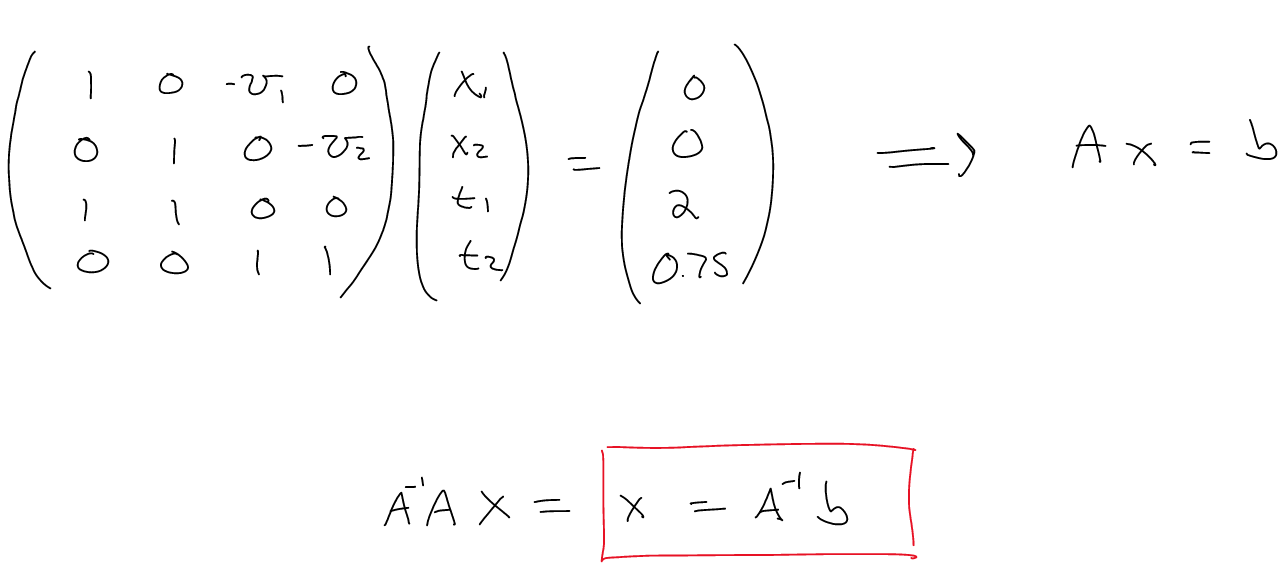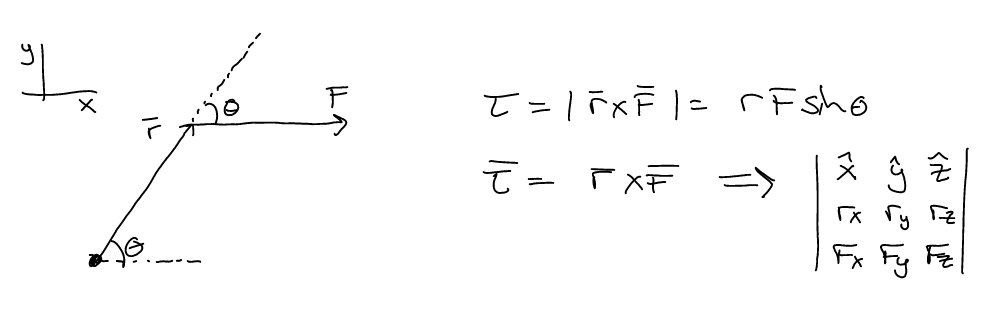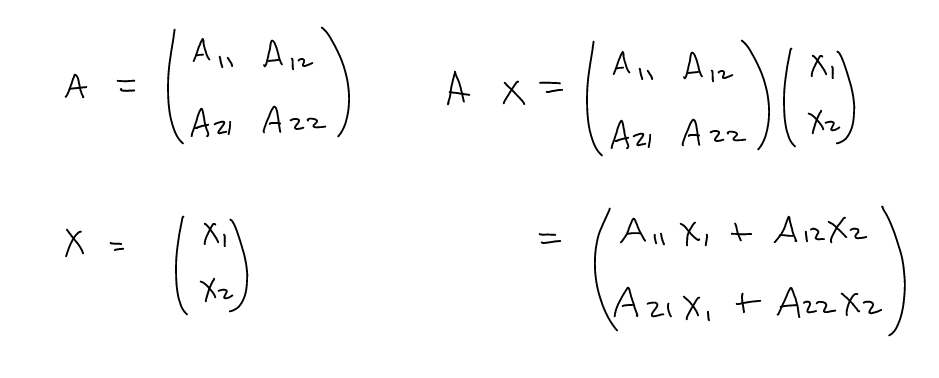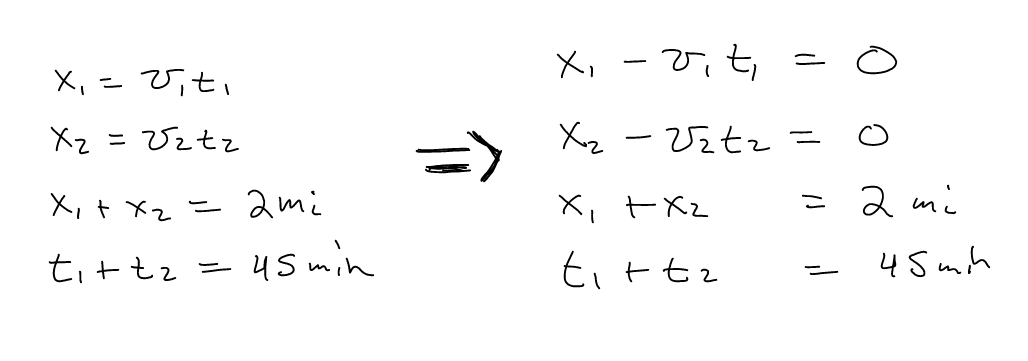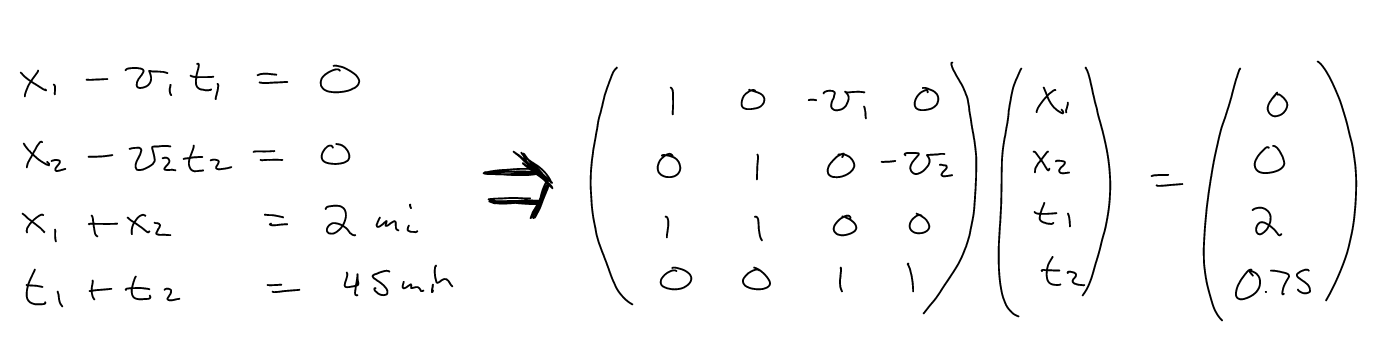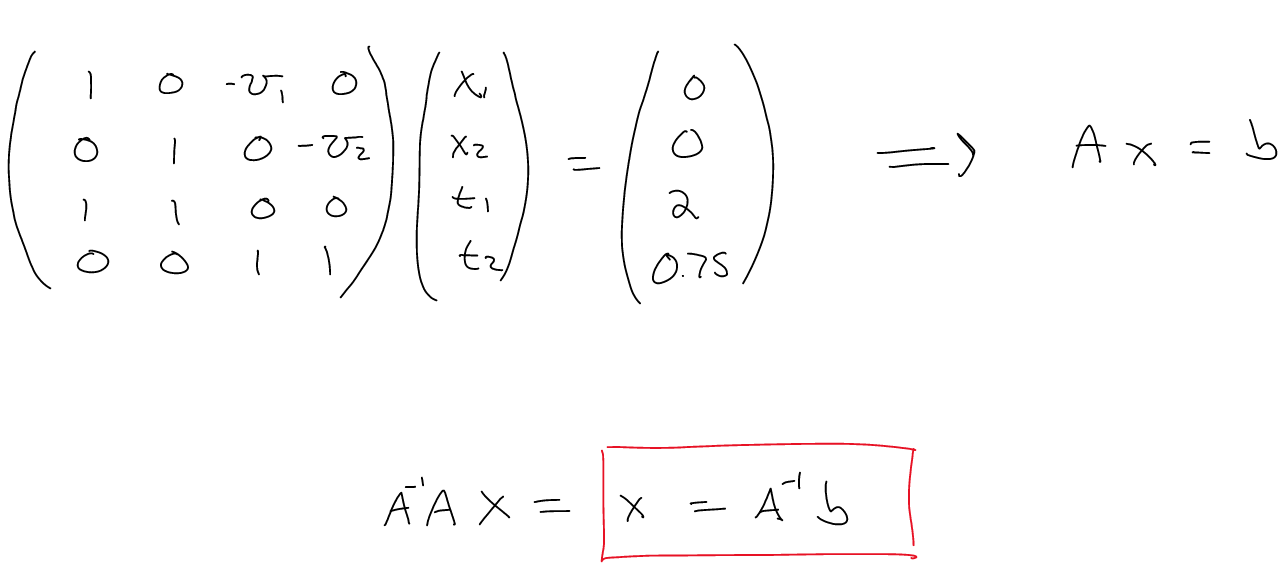Python
Part 1
Introduction
- Python is a programming language that has become very popular.
- there are literally thousands of libraries written for Python
- It is simple and powerful
(like Gnuplot).
- used for automating tasks that would be difficult or “messy” in
shell scripts.
- used to process “big data”, machine learning, and build physics
simulations.
- used to write professional quality software (Google, YouTube,
Spotify, etc)
Installing
Python usually comes installed by default on Linux machines.
But, if not, on Ubutnu we would run
$ sudo apt install python3 python-is-python3
- We want Python version 3.
- We want
python to be an alias for
python3.
First “Program”
- Python is an “interpreter”.
- That means we can write a script and tell Python to run the commands
in the script.
- It also means anything we can do in a python script we can do at the
command line.
- We can also tell Linux run the script with Python using the
shebang.
Demo: Hello World
demos/02-helloworld.sh
Part 2
Python as a Calculator
- We can use python as a powerful calculator.
The force of gravity between two masses is given by \[
F = \frac{G m_1 m_2}{r^2}
\]
What will the gravitational force between a 100 kg and a 200 kg mass
placed 0.1 meter apart?
Recall that \(G = 6.67430\times
10^{-11} \text{m}^3 \text{kg}^{-1} \text{s}^{-2}\)
Part 3
Python as a Calculator
Variables
What will the gravitational force between a 500 kg and a 200 kg mass
placed 0.01 meter apart?
. . .
- Variables are a way for us to store a number and give it a
name.
- We don’t want to type
6.67430e-11 every time we do a
new calculations.
- We can use a variable to store the number, and then use the
name.
Variables in Python are different than bash:
- We can store the actual number, not just the text.
- We don’t have to use a
$ to get the variables
value.
demos/04-variables.py
Python as a Calculator
Functions
What will the gravitational force between a 5000 kg and a 2500 kg
mass placed 0.2 meter apart?
. . .
- Functions are a way for us to store a calculation and give
it a name.
- We don’t want to type out G*m1k*m2/r**2 every time we want to do a
calculation (see a pattern?)
Functions are different in Python than Gnuplot:
- We have to declare the function using
def functionname(args):
- Then we “return” the functions value.
Python as a Calculator
Part 4
Python as a Calculator
Modules
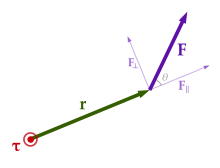
The torque generated by a force is given by the cross product of the
lever arm and the force \[
\vec{\tau} = \vec{r} \times \vec{F}
\]
The magnitude of the torque will be \[
\tau = \left| \vec{r} \times \vec{F} \right| = r F \sin\theta
\]
. . .
Python as a Calculator
Modules
- Python libraries are called “modules”
- Modules are just pieced (sometimes large) of code that somebody else
has already written to do something useful.
- The trigonometry functions are in the
math module has
functions for evaluating trig functions.
./demos/06-modules.sh
Standard Library
The “Python Standard Library” is a collection of modules (like the
math module) that are included with Python.
There are dozens of librarys…
https://docs.python.org/3/library/
Part 5
Useful Modules: pint
- Pint is a python
module for doing unit conversions and dimensional analysis.
- It can do unit conversions, and check that the dimensions of a
quantity are correct.
- This makes python very useful as a calculator.
- But we need to install it…
What is the gravitational force between a 200 lb mass and a 150 lb
mass separated by 6 ft?
./demos/07-pint.sh
Local installs and virtual environments
- Python supports installing modules into a “system” directory or a
“local” directory.
- “Virtual environments” are a way to install modules into a local,
self-contained, environment.
- In Ubuntu 24.04, there was a change. You can no longer install
packages into the system directory without using apt.
Local installs and virtual environments
Steps to create and use a virtual environment:
python -v venv venv Create a new virtual environment in
a directory named venvvenv/bin/pip install <module> Install modules
into the virtual environmentvenv/bin/python my_script.py Use the environment to to
run a scriptsource venv/bin/activeate Setup shell to use the
environment by default
Part 6
A better interpreter
- When we run
python3 with no arguments, we get a command
prompt.
- The python interpreter starts reading text from standard input and
running the python code we type in.
- This is fine, but there are more advanced interfaces…
./demos/08-ptpython.sh
Part 7
Useful Modules: pyErrorProp
- In physics, we often need to perform some calculation with measured
values that have uncertainty.
- We need to quantity the uncertainty in our calculated values.
- We do this by “propagating error”.
pyErrorProp is a python module for doing error
propagation.
- Given a user-defined function,
pyErrorProp will compute
the uncertainty in the returned value of the function based on the
uncertainty of the arguments passed in.
Error Propagation Example
If you measure the length of a table to be 150 centimeter, plus or
minus 0.5 centimeter, and the width to be 80 centimeter, plus or minus
0.5 centimeter, what is the area of the table top?
Error Propagation Example
Straight out of the Physics Lab Error Analysis Reference:
You drop a ball bearing 10 times from a height of 3 meter, plus or
minus 0.5 cm, and measure the fall time to be 0.79 s, plus or minus 0.02
s. What is \(g\)? Recall: \(g = \frac{2h}{t^2}\)
Another group performs the same experiment and computes \(g = 10.6 \pm 0.4\) meter per second
squared. Are your measurements consistent?
Useful Modules: numpy
Numerical Python
(numpy) is a (large) collection of tools for doing
numerical calculations in python.
For us, it provides tools for doing vector operations (compute the
dot product, cross product, etc), matrix-vector operations (multiply a
vector by a matrix), and matrix operations (invert matrix, compute eigen
values and eigen vectors, etc)
Useful Modules: numpy
Vector operations
How much work is done by a force \(\vec{F} = 5 N \hat{x}\) if the object that
the force is exerted on is displaced \(\Delta
\vec{r} = 2 m \hat{x} + 4 m \hat{y}\).
Recall: \(W = \vec{F} \cdot
\Delta\vec{r}\)
Compute the torque generated by a for \(\vec{F} = 5 N \hat{x}\) exerted on a lever
arm \(r = 10 cm \hat{x} + 10 cm
\hat{y}\)
Recall: \(\vec{\tau} = \vec{r} \times
\vec{F}\)
Also: \(\tau = r F
\sin\theta\)
Useful Modules: numpy
Work Calculation
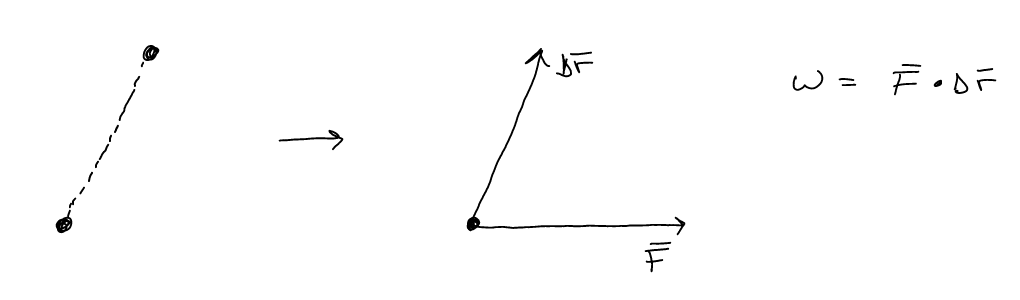
Useful Modules: numpy
Torque Calculation
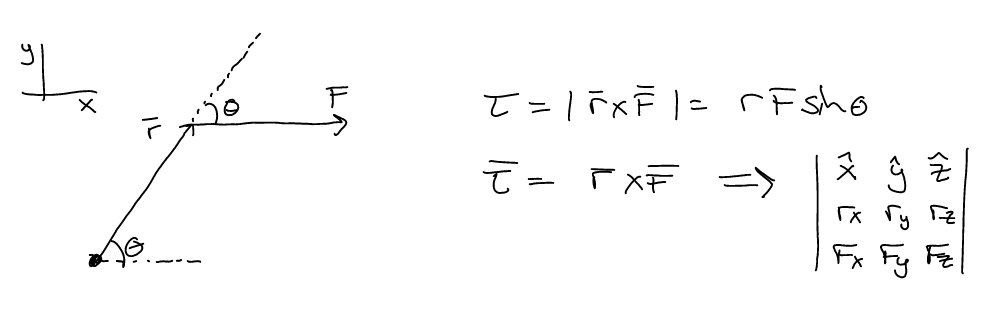
Useful Modules: numpy
Matrix-vector operations
Matrix-vector multiplication is as simple as creating a matrix and
“dotting” it with a vector.
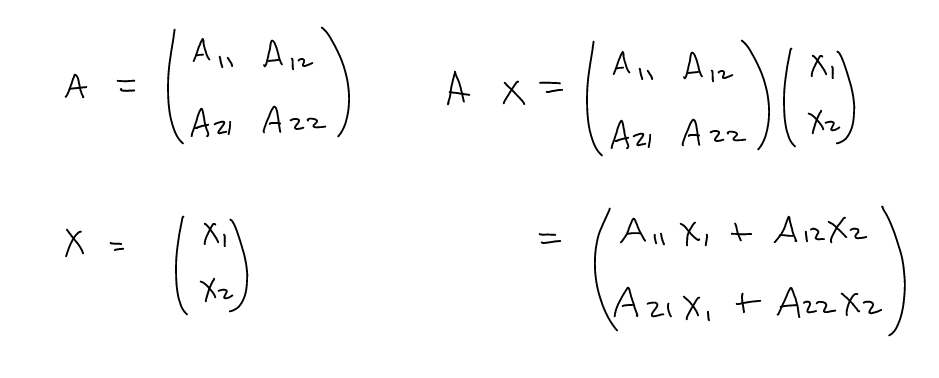
Useful Modules: numpy
Matrix operations
Systems of equations can be represented as matrix equations.
- Jack goes out for a run and plans to run 2 miles. He starts out
running at a brisk 10 mile/hour pace, but soon tires and ends up walking
the rest of the way at 2 mile per hour. It takes Jack 45 minutes to
travel the two miles. At what time did Jack stop running?
Useful Modules: numpy
System of Equations
- Jack goes out for a run and plans to run 2 miles. He starts out
running at a brisk 10 mile/hour pace, but soon tires and ends up walking
the rest of the way at 2 mile per hour. It takes Jack 45 minutes to
travel the two miles. At what time did Jack stop running?
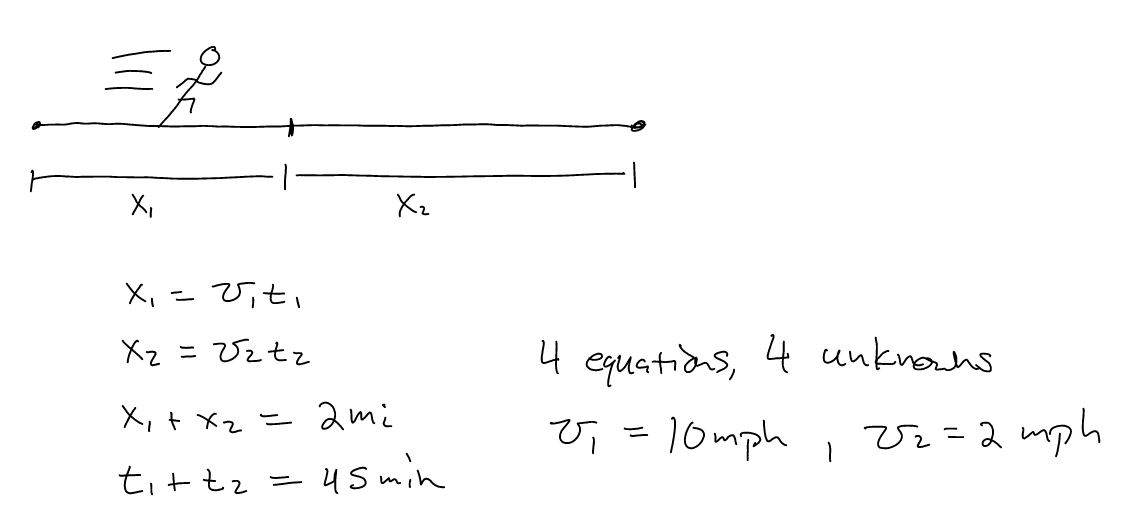
Useful Modules: numpy
System of Equations
- Jack goes out for a run and plans to run 2 miles. He starts out
running at a brisk 10 mile/hour pace, but soon tires and ends up walking
the rest of the way at 2 mile per hour. It takes Jack 45 minutes to
travel the two miles. At what time did Jack stop running?
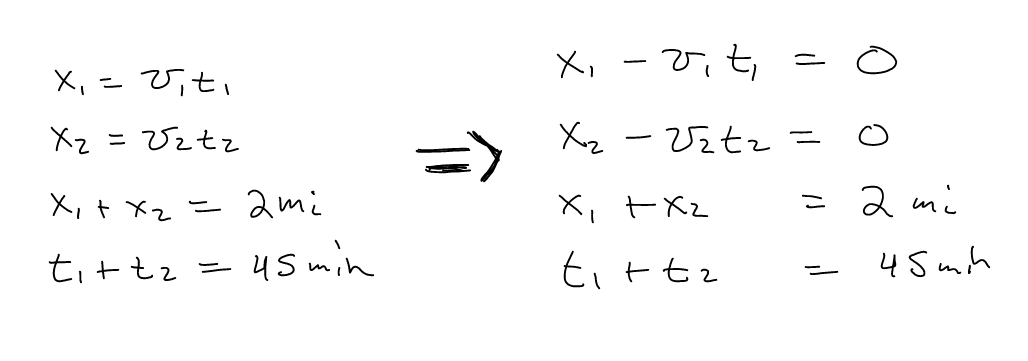
Useful Modules: numpy
System of Equations
- Jack goes out for a run and plans to run 2 miles. He starts out
running at a brisk 10 mile/hour pace, but soon tires and ends up walking
the rest of the way at 2 mile per hour. It takes Jack 45 minutes to
travel the two miles. At what time did Jack stop running?
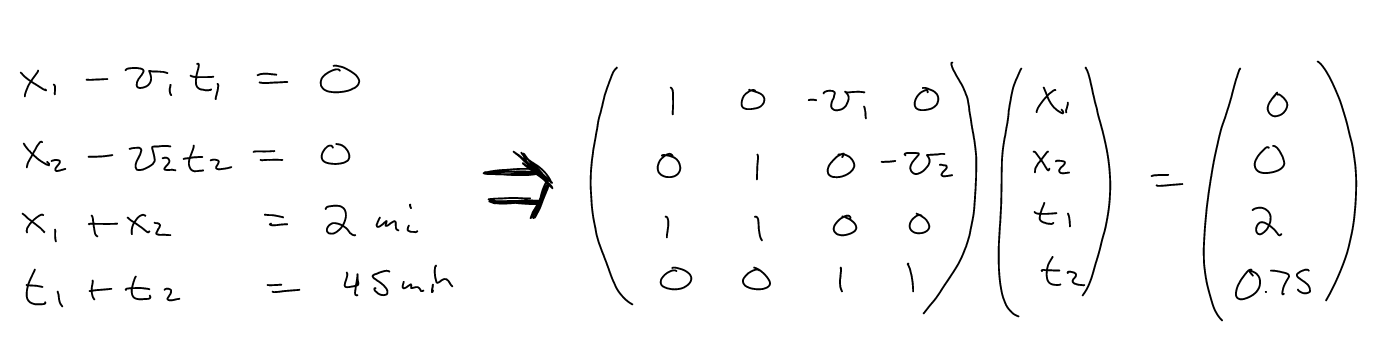
Useful Modules: numpy
System of Equations
- Jack goes out for a run and plans to run 2 miles. He starts out
running at a brisk 10 mile/hour pace, but soon tires and ends up walking
the rest of the way at 2 mile per hour. It takes Jack 45 minutes to
travel the two miles. At what time did Jack stop running?