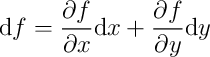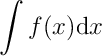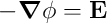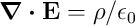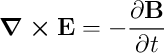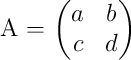LaTeX
First
$ sudo apt install texstudio
Terminology
- Content vs. Formatting
- Content: What your document says.
- Formatting: How your document looks.
- Typesetting: Formatting a document for printing.
- Markup: Special keywords that describe the structure of your
document
- Word Processor: A program that manages content and formatting
together (WYSIWYG)
- Compile: LaTeX reads a text file and generates a PDF. Its almost
like compiling a program.
What is LaTeX?
- Content vs. Formatting
- Content: What your document says.
- Formatting: How your document looks.
- Typesetting: Formatting a document for printing.
- Markup: Special keywords that describe the structure of your
document
- Word Processor: A program that manages content and formatting
together (WYSIWYG)
- Compile: LaTeX reads a text file and generates a PDF. Its almost
like compiling a program.
LaTeX is a markup language and
compiler that typesets your document
and generates a PDF.
Motivation
Math
- Very common in the math and science
communities.
- It just looks professional…
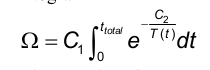 vs.
vs. 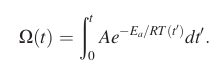
Support for automatic cross-references.
Support for automatic bibliography generation.
Plain Text can be edited with simple scripts.
- It is much more fun to use.
Separate content from typesetting.
- You write a plain text file with your content.
- You use markup to define the structure of your document.
- LaTeX generates a PDF with your content formatted in a specific
style (and it is very easy to change styles).
De-Motivation
- Figures
- Can only import pictures in certain file formats.
- Cannot just click and drag to desired position.
- Separate content from typesetting.
- The LaTeX compiler takes care of formatting. You have to convince it
to do what you want.
- It can be a pain at times.
- Deciphering error messages is a nightmare.
_

Our first document
Let’s fire up texstudio…
Note: You can create and compile your document without
texstudio (I use vi and Makefiles)
But, texstudio has some useful features.
The pdflatex compiler
Let’s compile our latex without texstudio.
LaTeX commands
LaTeX’s markup consists of commands and
environments.
Commands:
\commandname[options]{argument1}{argument2}- Examples:
\nabla: insert the del operator \(\nabla\)\int: insert an integral sign \(\int\)\begin{equation}: open an equation
environment\end{equation}: close an equation
environment\emph{some text}: add emphasis (usually itallics) to
text\section{Section Name}: create a section header\frac{x}{y}: render a fraction \(\frac{x}{y}\)\documentclass[10pt,letterpage]{article}: set the
document class to article and use 10pt font on a letter
page.
Environments:
- LaTeX “environments” are sections of text with some special
context.
- They are identified with a
\begin{environment_name} and
\end{environment_name}
LaTeX commands
Lets:
- set the title
- set the author
- add a section
- add an equation
- inline
- on its own line
- with a number
Equations: Math Mode
LaTeX has a “text mode” and a “math mode”.
In “math mode”, text is rendered as math…correctly
\[
y = mx + b
\]
vs.
\[
\text{y = mx + b}
\]
Some commands are only available in “math mode.”
There are multiple ways to activate “math mode”
- Single dollar signs:
$y = mx + b$
- Double dollar signs:
$$y = mx + b$$
- The
equation environment
- The
align environment
Equations
Inline math with single dollar signs, $y = mx + b$. The dollar signs open up "math mode"
Double dollar signs
$$y = mx + b$$
put the equation on its own line.
The equation environment will put an equation on its own line and give it a number
\begin{equation}
y = mx + b
\end{equation}
The align environment (in the amsmath package) will align multiple equations,
and add numbers.
\begin{align}
y & = mx + b \\
mx + b & = y
\end{align}
The starred equation and align environments wont add equation numbers
\begin{equation*}
\end{equation*}
\begin{align*}
y & = mx + b \\
mx + b & = y
\end{align*}
We can also choose specific equations that we dont want to number
\begin{align}
y & = mx + b \\
mx + b & = y \nonumber \\
y & = mx + b
\end{align}
Equations
Let’s:
add Maxwell’s Equations \[
\nabla \cdot \vec{E} = \frac{\rho}{\epsilon_0} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{B} = 0 \\
\nabla \times \vec{E} = - \frac{\partial \vec{B}}{\partial t} \\
\nabla \times \vec{B} = \mu_0\left( \vec{J} + \epsilon_0 \frac{\partial
\vec{E}}{\partial t} \right)
\]
align these equations
remove the numbers
remove just one of the numbers
Cross-references
We often need to reference a specific equation in our writing. We
also need to reference sections or subsections, tables, figures, etc.
These are cross-references.
To cross-reference something, we have to
- label what we want to reference with
\label{label_text}
- reference the label in your text with a
\ref{label_text}
Lets:
- add reference to an equation
- add reference to a section
Tables
\begin{table}
\begin{tabular}{ccc}
year & make & model \\
\hline
1978 & Chevrolet & Suburban \\
1973 & Chevrolet & Monte-Carlo \\
1977 & Chevrolet & Silverado \\
1992 & Chevrolet & Camaro \\
\end{tabular}
\caption{\label{tab:cars} List of cars driven by Clark in high school.}
\end{table}
Let’s:
- Create a table
- Add a caption
- Reference it in our text
_
LaTeX Libraires: Packages
- LaTeX has libraries that provide useful commands and/or
environments.
- To use a package, we have to have it installed, and we have to
include it.
- Many packages are installed by default.
- We include packages with the
\usepackage{...}
command
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amsmath}
...
Useful Packages
amsmath:fullpage:geometry:siunitx: docs (in
texlive-science)physics: docs (in
texlive-science)hyperref: docs
amsmath, fullpage, and
geometry
- We are already using
amsmath, it provides the
align environment
- The
fullpage package makes the margins more
reasonable.
- The
geometry package gives use full control over the
margins.
siunitx
siunitx is a packages for formatting units.
It solves the problem of formatting units inside of math mode
correctly.
If your travel 60 m in 2 s, then your velocity velocity is $30 \frac{m}{s}$
($3000 \frac{ \text{cm} }{ \text{s} }$).
In 1 hour, you will have travelled
\begin{equation}
x = v t = 30 \frac{\text{m}}{\text{s}} \text{hr}
\end{equation}
If your travel \SI{60}{\minute} in \SI{2}{\second}, then your velocity velocity is \SI{30}{\meter\per\second}
(\SI{3000}{\centi\meter\per\second}).
In 1 hour, you will have travelled
\begin{equation}
x = v t = \SI{30}{\meter\per\second\hour}
\end{equation}
siunitx Examples
\SI{9.8}{\meter\per\second\squared}
\SI{100}{\degree C}
\SI{2.3e7}{\gram\per\meter\cubed}
siunitx Options
\usepackage[per-mode=fraction]{siunitx} will format
units in fractions (instead of negative exponents).
hyperref
The hyperref package allows you to insert links to web pages in your
document.
\url{https://google.com} will create a link using the
URL as its text.\href{https://google.com}{Google} will create a link
using Google for the text.
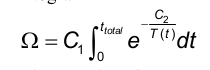 vs.
vs. 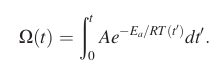
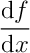
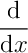
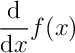
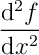
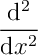
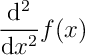
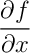
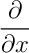
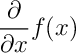
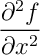
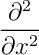
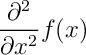
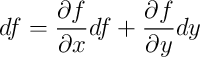 (not quite correct)
(not quite correct)